Abstract
As biopharmaceutical companies face increasing pressure to decrease the overall drug development timeline, analytical researchers find themselves finalizing methods earlier in development with less material on hand. Of all the analytical methods to be developed, charge variant analysis methods used to monitor post-translational modifications (PTMs), require the longest time commitment. Quickly finding a robust, stabilityindicating method that can monitor charge variants is an ongoing analytical challenge.
Introduction
HPLC-based ion-exchange chromatography (IEX) methods commonly analyze biotherapeutics in their native state. These methods can be optimized with regard to column stationary phase, mobile phase pH, type of and concentration of buffer salts, gradient conditions, and a host of other parameters. Development of a suitable method for a single molecule can easily span weeks to months.
Capillary Isoelectric Focusing (cIEF) charge variant methods generally analyze biotherapeutics in a denatured state. Development time is often much shorter compared to IEX due to fewer parameters to optimize, including buffer additives, concentration and focusing time. However, when analyzed in a denatured state, generated stability data does not always trend as well as native state stability data.
Capillary Zone Electrophoresis (CZE) combines the benefits of a native state analysis with the speed and resolution expected of a capillary electrophoresis method. Using a widely universal buffer,1 this technique requires little to no method development, has a simple sample preparation and a higher analytical throughput than IEX or icIEF.
The SCIEX CZE Rapid Charge Variant Analysis Kit (P/N C44790) provides high resolution, high sensitivity CZE separations.
Charge Heterogeneity in Minutes
- Quantify charge variants in their native state
- Little-to-no method development
- Dilute, shoot and prepare for your next CE application
- Platform capable methodology
Demonstrated here are the charge variant analyses of multiple commercially available monoclonal antibodies on the PA 800 Plus platform using this kit. This method can easily be applied to therapeutic proteins such as antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), pre-clinical monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), and fusion proteins with little to no method development. Additionally, it can be easily modified to suit more specific user criteria.
Methods
Instrumentation
All experiments were performed on the PA 800 Plus Pharmaceutical Analysis System (SCIEX). A Pre-Assembled Cartridge (SCIEX P/N A55625) was used for the separation of all three commercially available monoclonal antibodies: Herceptin® (trastuzumab), Rituxan® (rituximab) and Remicade® (infliximab).
Reagents
Reagents used to prepare the samples and analysis buffers were provided in the CZE Rapid Charge Variant Analysis Kit (SCIEX P/N C44790). The therapeutic proteins of Herceptin® , Remicade® and Rituxan® were purchased from Myoderm (Norristown, PA).
Sample Preparation
Herceptin® , Remicade® and Rituxan® were diluted to 1 mg/mL in CE Grade water (SCIEX P/N C48034).
Instrumentation
The capillary electrophoresis instrument used was a PA 800 Plus equipped with UV detection and a 214nm bandpass filter (SCIEX P/N 144437).
Separation and Analysis
Separations were performed at 1000 V/cm and injection was performed by pressure for 10 seconds at 0.5 PSI. The separation buffer used was from the CZE Rapid Charge Variant Analysis Kit (SCIEX P/N C44790). Data acquisition and analysis was done using 32 Karat software V10.
Results
To investigate the reproducibility of the assay, 10 injections of each molecule were made. The peak profile was stable and %RSDs of the total relative area percentages of acidic variants, basic variants and main peak were below 2% (tables 1-3).
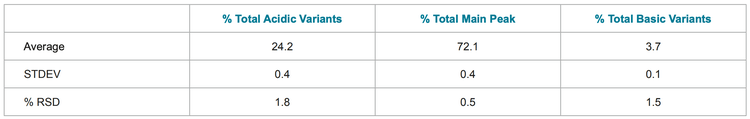
Conclusion
- Reproducible: CZE separations are shown to be reproducible through both replicate injections of commercial mAbs and an inter-company collaboration.2
- Platform capable: The simplicity of separation and optimal pH of the buffer allows for application to molecules across a broad pI range above 7.0.2
- Limited method development: Additional resolution can easily be obtained through the use of a longer bare-fused silica capillary, lower capillary temperature or separation voltage. Further development has focused on buffer pH and levels of additives.3
- High-Throughput: High-resolution separation can be achieved in approximately 5 minutes or less. With only two minutes of buffer replenishment in between injections, total sample analysis time can be completed in under 10 minutes.
References
- He, Y., Isele, C., Hou, W., Ruesch, M., J. Sep. Sci. 2011, 34, 548–555.
- Moritz, B., Schnaible, V., Kiessig, S., Heyne, A., Wild, M., Finkler, C., Christians, S., Mueller, K., Zhang, L., Furuya, K., Hassel, M., Hamm, M., Rustandi, R., He, Y., Solano, O. S., Whitmore, C., Park, S. A., Hansen, D., Santos, M., Lies, M., J. Chromatogr. B 2015, 983–984, 101–110.
- Moritz, B., Locatelli, V., Niess, M., Bathke, A., Kiessig, S., Entler, B., Finkler, C., Wegele, H., Stracke, J., Electrophoresis 2017, 38, 3136-3146.


