Abstract
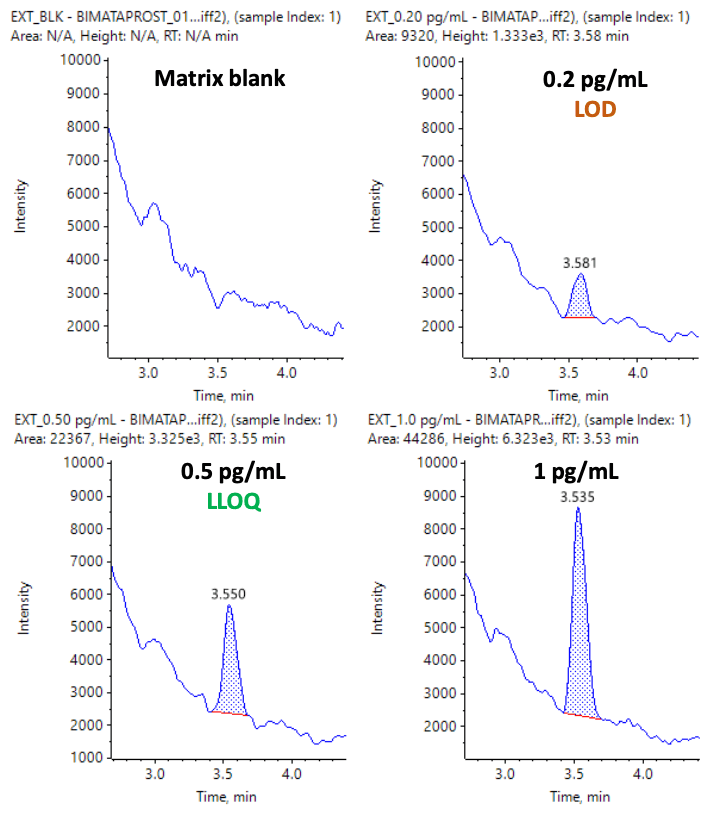
This technical note demonstrates a sensitive method for the quantitation of an ocular drug, bimatoprost, in human plasma. The method employs a simple liquid-liquid extraction sample preparation to separate bimatoprost from human plasma. A lower limit of quantitation (LLOQ) of 0.5 pg/mL was achieved with %CV <3% (Figure 1).
Introduction
Eye diseases, next to cardiovascular and respiratory diseases, are the most common among the general population. 1 Aging is one of the major risk factors for glaucoma, which leads to optic nerve cell damage and ultimately causes blindness. 2 Glaucoma develops when fluids cannot drain from the eye, leading to increased pressure. Common treatments include laser surgery or treatment with prostaglandin analogs and topical drugs (eye drops) such as bimatoprost and latanoprost.
Bimatoprost is a synthetic prostamide that is similar in structure to prostaglandin F2α (PGF2α). It functions by substituting an electrochemically neutral amide group for the carboxylic acid group in PGF2α. Glaucoma and other eye conditions caused by high blood pressure can be effectively treated with bimatoprost. The usual dosage is one drop of 0.03% bimatoprost. It predominantly resides in plasma and has an 88% plasma protein binding rate. Bimatoprost has an estimated Cmax of 60-80 pg/mL and the maximum plasma concentration is often reached in less than 10 minutes.5 Therefore, it is important to have a sensitive bioanalytical method for the quantitation of bimatoprost across a wide range of concentrations in biological matrices to support pharmacokinetic studies.4
The bioanalytical method described in this technical note uses 400 µL of human plasma and a simple liquid-liquid extraction procedure to detect low levels of bimatoprost.
Key features for the analysis of bimatoprost using the SCIEX 7500 system
- Sensitive and reproducible of quantitation of low-dose, high-potency drug modalities: Achieve a 0.50 pg/mL LLOQ for bimatoprost in human plasma with %CV <3%
- Low plasma consumption and simple sample preparation: Use a low sample volume of 400 µL of human plasma paired with a simple liquid-liquid extraction methodology to quantify bimatoprost
- Enhanced sensitivity unlocked: Improved front-end technology with the D Jet ion guide, OptiFlow Pro ion source and E Lens probe for enhanced ion generation, capture and transmission, enable users to reach their desired quantitative sensitivity
- Streamlined data management: Data acquisition and processing are integrated into SCIEX OS software, a 21 CFR Part 11 compliance-ready platform
Methods
Spiked sample preparation: Bimatoprost was spiked into 400 µL of human plasma at concentrations ranging from 0.2 to 500 pg/mL. A 100 µL aliquot of 0.1N sodium hydroxide in water was added to the sample and vortexed for 2 minutes. A 4 mL aliquot of 80:20 (v/v), ethyl acetate/n-hexane was added to the samples, vortexed for 10 minutes and centrifuged at 1204 rcf for 5 minutes. The supernatant was collected and dried under a nitrogen stream at 40°C. The dried samples were reconstituted using 150 µL of 30:70 (v/v), acetonitrile/5mM ammonium formate in water. A 20 µL sample injection was used for analysis.
Chromatography: An ExionLC system with a Phenomenex Kinetex XB-C18 column (2.1 x 100 mm, 1.7 µm, 100 Å) was used for chromatographic separation. The LC column was operated at 40°C. Mobile phase A was 5mM ammonium formate in water and mobile phase B was acetonitrile. Table 1 summarizes the LC gradient conditions used.
Mass spectrometry: Samples were analyzed using the SCIEX 7500 system equipped with the OptiFlow Pro ion source. The system was controlled by SCIEX OS software. The optimized source and MS parameters are listed in Table 2.
Data processing: Data processing was performed using SCIEX OS software, version 3.1.6. Peaks were automatically integrated using the MQ4 algorithm with a weighting of 1/x2 .
Quantitative performance
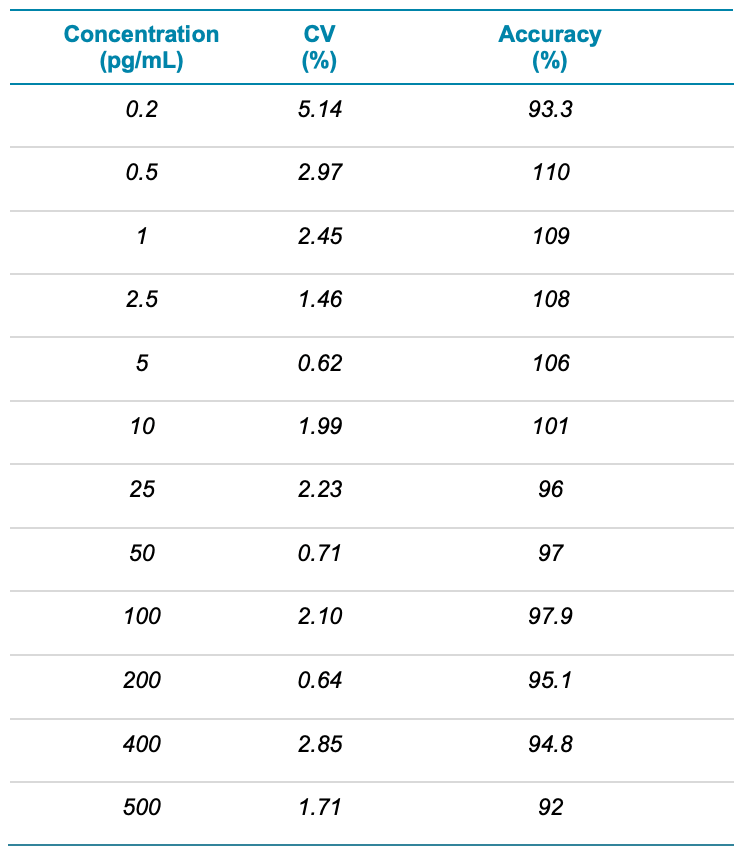
A calibration curve was analyzed for concentrations ranging from 0.2 to 500 pg/mL. To evaluate reproducibility, each calibration standard was analyzed in triplicate.
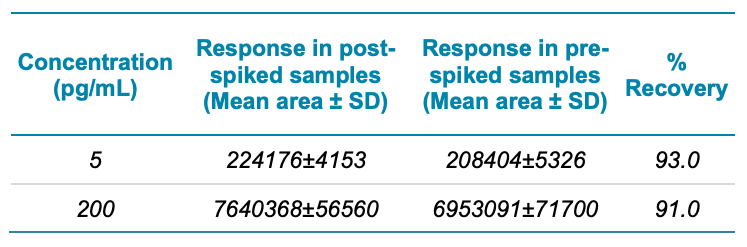
Bimatoprost in human plasma was quantified at an LLOQ of 0.5 pg/mL with an LOD of 0.2 pg/mL. No interferences were observed in the matrix blank (Figure 1). Linearity was achieved across concentrations ranging from 0.2 to 800 pg/mL with a correlation of determination (r2 ) of 0.994 (Figure 2). A linear dynamic range (LDR) of 3 orders of magnitude was achieved.
Analytical performance was evaluated based on the requirement that the accuracy of the calculated mean should be between 80% and 120% at the LLOQ and between 85% and 115% at higher concentrations. The %CV of the calculated mean concentration should be below 20% at the LLOQ and below 15% at all higher concentrations.3
The assay accuracy was within ±10% of the nominal concentration and the %CV was <6% (Table 3), including at the LOD. The calculated accuracy and %CV values were within the acceptance criteria at each concentration level (Table 3).
Compliance-ready SCIEX OS software
SCIEX OS software is a closed system and requires records and signatures to be stored electronically, meeting the regulations outlined by 21 CFR Part 11. SCIEX OS software can open raw data files from any visible storage location within a closed network by using designated processing workstations. Figure 5 illustrates the features of SCIEX OS software used for monitoring the audit trail, acquiring and processing data and configuring user access.
The audit trail feature enables users to audit critical user actions and locks in data integrity. The Central Administrator Console (CAC) feature allows users to centralize acquisition and processing using a single platform to maximize efficiency for multi-instrument laboratories, independent of compliance standards. The configuration module allows users to assign roles and access as the administrator, method developer, analyst and reviewer.

Conclusion
- An LLOQ of 0.50 pg/mL was achieved to quantify bimatoprost in human plasma with an LOD of 0.2 pg/mL
- Linearity was achieved at concentrations ranging from 0.2 pg/mL to 500 pg/mL with an r2 of 0.994
- Desired LLOQ (0.5 pg/mL) for bimatoprost was achieved with 400 µL of human plasma
- The method demonstrated accurate and highly reproducible quantitative performance (%CV <6%) for all concentration levels, including the LOD
- Sensitivity was achieved on the SCIEX 7500 system with an improved front-end technology for better ion generation, capture and transmission
- SCIEX OS software is compliance-ready to support 21 CFR Part 11 and integrates with a triple quadrupole mass spectrometer to support data acquisition, processing and management on a single platform.
References
- Trends in development and quality assessment of pharmaceutical formulations - F2α analogues in the glaucoma treatment. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 180, Jan 2023, 106315.
- The number of people with glaucoma worldwide in 2010 and 2020. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 90, 262–267.
- Bioanalytical Method Validation, May 2018.
- Clinical pharmacology and biopharmaceutics review(s), 211911Orig1s000.
- Assessment report for Lumigan, 7 Jan 2010, Doc. Ref:EMA/105752/2010



