Introduction
Bile acids are involved in a wide range of biological functions including lipid resorption, immunological functions and metabolic regulation. They are part of a large family of molecules that consist of a four-ring steroid structure with various side chains.
The challenge:
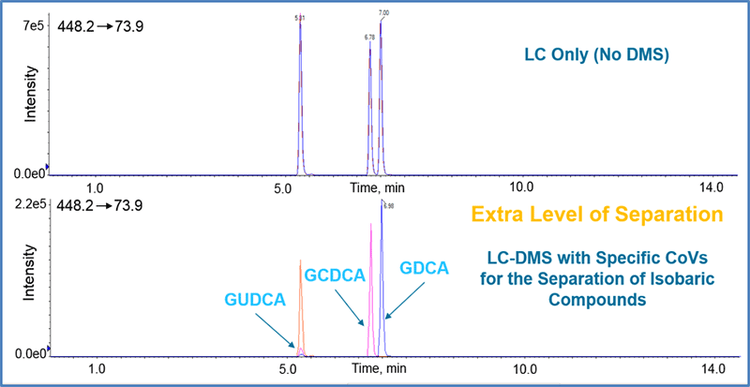
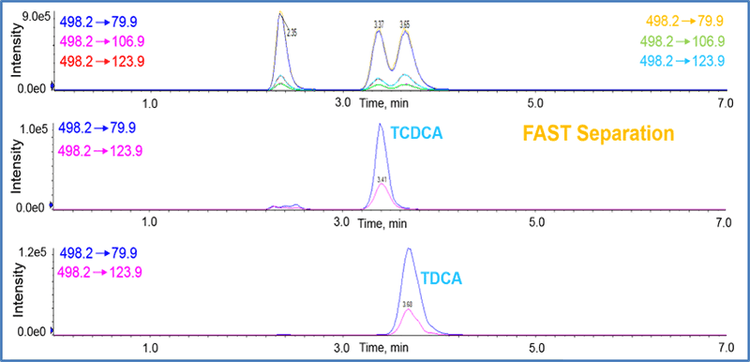
Through metabolic transformations, isomeric and isobaric variants of bile acids are generated, which makes the unequivocal identification and quantification of these individual chemical species difficult.
The solution:
Here, differential ion mobility spectrometry (DMS, SelexIONTechnology) was used as a methodology for the separation of two groups of bile-acids isomers. SelexION Technology is an ion mobility technology which separates molecules based on their dipole moment instead of m/z. This separation was used in conjunction with liquid chromatographic separation (LC-DMS-MS) as well as with fast isocratic separations to investigate bile acids. While the combination with chromatographic separation may improve selectivity for bile acid quantitation, the separation power of SelexION Technology is sufficient for a clear separation of isomers, enhancing the selectivity of the measurement, and enables fast quantification with minimal LC separation.
References
- Differential mobility separation for improving lipidomic analysis by mass spectrometry - SelexION® Technology on QTRAP® Systems. SCIEX technical note RUO-MKT-02-4802-A.
