Abstract
Lopinavir and ritonavir are two protease inhibitors (class of anti-viral drugs) often used in a fixed-dose combination, along with other medications, for prevention and treatment of HIV/AIDS. Monitoring of lopinavir and ritonavir in human plasma is needed to ensure proper therapeutic levels are maintained. A very high throughput bioanalytical method (3 sec/sample) for the simultaneous analysis of ritonavir and lopinavir in human plasma is described using the Echo MS platform. Using a simple liquid-liquid extraction (LLE) for sample preparation, the assay provided very sensitive, accurate and reproducible results.
Introduction
Protease inhibitors (PIs) are a class of anti-viral drugs that prevent viral replication by selectively binding to viral proteases and inhibiting their function. The development of PI-based therapies has been of enormous benefit to people infected with HIV. Used in combination with other drugs, PIs have dramatically reduced the number of people who become ill from HIV-related opportunistic infections or who die from AIDS.
Unfortunately, the effectiveness of protease inhibitors can fade over time. Mutations during viral replication can result in viruses that produce new, different proteases that are not targeted by current PI therapies.1 The best way to avoid this drug resistance is to reduce or stop HIV replication. With less HIV replication, there is less of a chance of a new strain that is resistant to anti-HIV drugs. To keep HIV levels as low as possible, PIs are typically taken in combination with at least two other anti-HIV drugs. Such combination therapies are referred to as highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART).2
Lopinavir and ritonavir are two protease inhibitors that are often used as part of a fixed-dose combination, and serve as the model compounds in this study.
Acoustic Ejection Mass Spectrometry (AEMS), as implemented in the Echo® MS System with a SCIEX Triple Quad™ 6500+ LC-MS/MS system, offers clear benefits for quantification of lopinavir and ritonavir in human plasma. Requiring minimal sample preparation and no chromatographic separation, it provides high sample throughput without sacrificing robustness or reproducibility. The Echo® MS System combines Acoustic Droplet Ejection technology with an Open Port Interface (OPI) to deliver nanoliter sample volumes with minimal carryover. The small sample size reduces matrix suppression and facilitates easy sample preparation.
Key features of the Echo® MS System for high-throughput bioanalysis quantification
- Ultra-fast 3 sec/sample analyses provide high throughput for quantifying large number of samples
- Liquid-liquid extraction (LLE) sample preparation ensures excellent quantitative accuracy
- Exceptional sensitivity of the Echo® MS System yields high quality data at all concentration levels
Experimental details
Sample preparation: Lopinavir and ritonavir (Sigma Aldrich) were spiked into human plasma (BioIVT) samples in the range of 0.5 ng/mL to 250 ng/mL each. Samples were processed using a liquid-liquid extraction method as follows. 0.5 mL of di-isopropyl ether was added to 0.1 mL aliquots of spiked plasma. Samples were vortexed for 1 minute followed by centrifugation at 12,000 rpm for 5 minutes. 0.4 mL of supernatant liquid was collected and dried under a nitrogen stream. Samples were reconstituted in 100 µL of 25% v/v methanol in water and transferred to a 384‑well plate for analysis by AEMS. Plates are available from Beckman Coulter Life Sciences.
Acoustic ejection method: Methanol with 0.1% v/v formic acid was used as carrier solvent at a flow rate of 425 µL/min. 50 nL sample volumes were ejected into mass spectrometer for analysis.
Mass spectrometry: The Echo® MS System included a SCIEX Triple Quad 6500+ LC-MS/MS system and was controlled by SCIEX OS Software 1.6.10. The optimized MS parameters are listed in Table 1.
Results
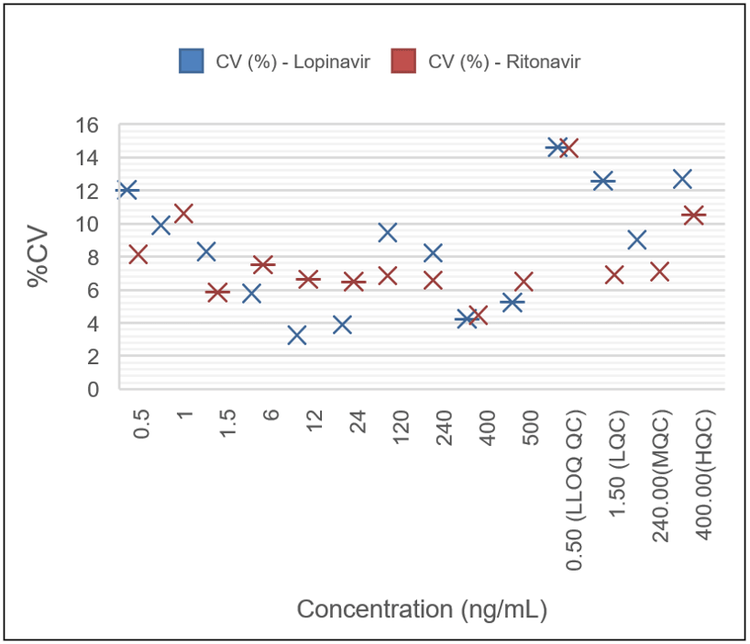
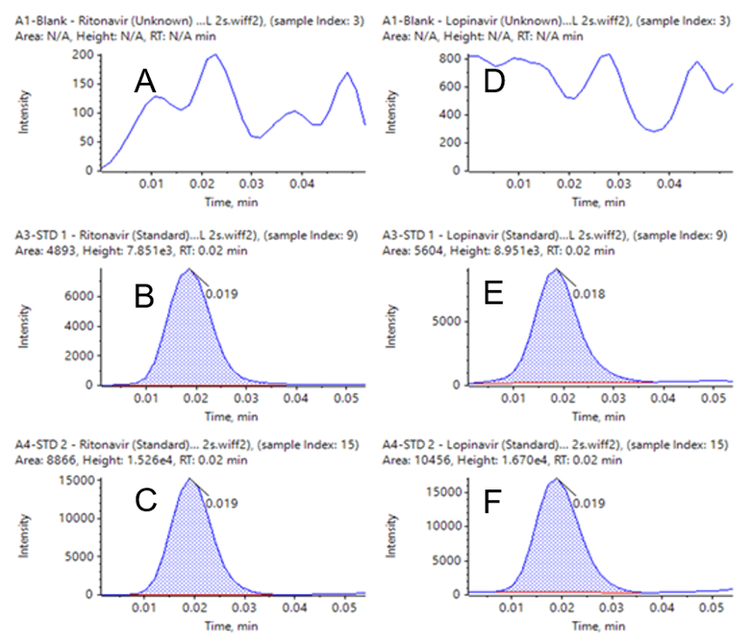
Samples for the calibration curves, along with quality control samples, all analyzed in six replicates, demonstrated the high reproducibility of AEMS when combined with liquid-liquid extraction. Excellent %CVs were achieved across all concentration levels with no interference in blank human plasma samples (Figure 1). Even at the extremely short analysis time of 3 seconds per sample, the method yielded LLOQs of 0.5 ng/mL for both lopinavir and ritonavir. As summarized in Tables 2 and 3, the assay accuracy was 85.31–112.34% for ritonavir and 85.51–113.52% for lopinavir. Accuracies and %CVs were well within standard acceptance criteria for all tested samples.
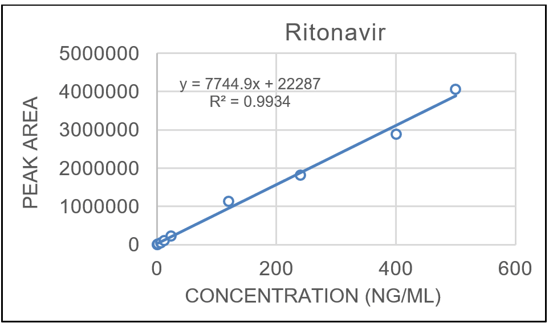
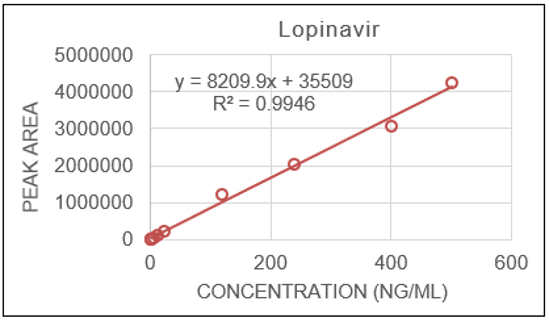
The calibration curve covered approximately 3 orders of magnitude (0.5–250 ng/mL) for both analytes and displayed linearity with regression coefficients (r2) of 0.9934 for ritonavir and 0.9946 for lopinavir using a weighting of 1/x2 (Figures 2 and 3).
Samples were analyzed without internal standards for this assay. Use of labeled internal standards might further improve these results.
Conclusions
- The Echo® MS System produced very sensitive, accurate and reproducible results for the simultaneous quantitative analysis of lopinavir and ritonavir in human plasma
- The very short analysis time (3 sec/sample) enabled rapid generation of quantitative data for high numbers of samples
- The assay showed great reproducibility without using labeled internal standards, but use of labeled internal standards is recommended to further improve these results
References
- Koehn J, Ho RJY. (2021) Novel Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for Simultaneous Detection of Anti-HIV Drugs Lopinavir, Ritonavir, and Tenofovir in Plasma. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 58 (5), 2675-2680.
- Mishra TD, Kurani H, Singhal P, Shrivastav PS, (2012) Simultaneous Quantitation of HIV-Protease Inhibitors Ritonavir, Lopinavir and Indinavir in Human Plasma by UPLC–ESI-MS-MS, Journal of Chromatographic Science, 50 (7), 625–635.
- Jaiswal S, Sharma A, Shukla M, Lal J, (2017) Simultaneous LC–MS-MS Determination of Lopinavir and Rifabutin in Human Plasma, Journal of Chromatographic Science, 55 (6), 617–624.



