Abstract
A robust method for the bioanalysis of alprazolam in plasma using a stable labeled internal standard using the Echo MS system is presented. Very high throughput was achieved, with 1 sample analyzed every 2 seconds, with very good accuracy and reproducibility.
Introduction
Benzodiazepines are often used to treat anxiety, insomnia and central nervous system disorders. They belong to the class of depressant drugs, acting on GABA receptors to dampen neural pathway excitation and consequently provide a calming effect.1 They are among the most common prescribed psychiatric medications. However, benzodiazepines are often accompanied by other drugs of abuse and detected alongside opioids in many overdose cases and fatalities.2
Alprazolam is the most commonly prescribed benzodiazepine for anxiety and panic disorders.3 As such, rapid, high-throughput detection of alprazolam in plasma is critical to forensic and clinical toxicology. LC-MS analysis strategies can be time consuming to develop and implement as they typically require lengthy and costly solid-phase extraction (SPE) sample preparation. Acoustic Ejection Mass Spectrometry (AEMS) offers a clear alternative for analysis of alprazolam in plasma. Requiring minimal sample preparation and no chromatographic separation, it provides increased sample throughput without sacrificing robustness or reproducibility.
The Echo® MS System with a SCIEX Triple Quad™ 6500+ Mass Spectrometer provides sensitive, high-throughput quantification of alprazolam. The system combines Acoustic Droplet Ejection technology with an Open Port Interface (OPI) to deliver nanoliter sample volumes with minimal carryover. The small sampling size reduces matrix suppression and facilitates easy sample preparation.4
Key features of the Echo® MS System for high-throughput bioanalysis quantification
- Ultra-fast 2 sec/sample analyses provide high throughput for quantifying large numbers of samples
- Liquid-liquid extraction (LLE) sample preparation ensures excellent quantitative accuracy
- Exceptional sensitivity of the Echo® MS System yields high quality data at all concentration levels
Experimental details
Sample preparation: Alprazolam was spiked into human plasma in the range of 0.5 ng/mL to 250 ng/mL along with 50 ng/mL of internal standard (alprazolam D5). Samples were processed using a liquid-liquid extraction method as follows. 1 mL of di-isopropyl ether was added to 0.3 mL aliquots of spiked plasma. Samples were vortexed for 1 minute followed by centrifugation at 12,000 rpm for 5 minutes. 0.8 mL of supernatant liquid was collected and dried under a nitrogen stream. Samples were reconstituted in 100 µL of 25% v/v methanol in water and transferred to a 384-well plate for analysis by AEMS. Plates are available from Beckman Coulter Life Sciences.
Acoustic ejection method: Methanol was used as carrier solvent in this assay at 425 µL/min. 50 nL sample volumes were ejected into the mass spectrometer for analysis.
Mass Spectrometry: The Echo® MS System includes a SCIEX Triple Quad 6500+ System and was controlled by SCIEX OS Software 1.6.10. The optimized MS parameters are listed in Table 1.
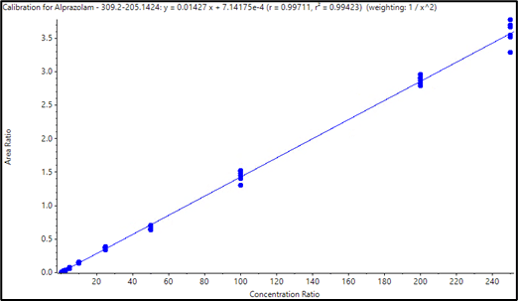
Data processing: Data processing was performed using SCIEX OS Software. A calibration curve was generated with six replicates at each concentration level to evaluate ejection reproducibility and accurately determine the lower limit of quantification (LLOQ). The calibration curve is shown in Figure 2 and a quantification summary is listed in Table 2.
Results
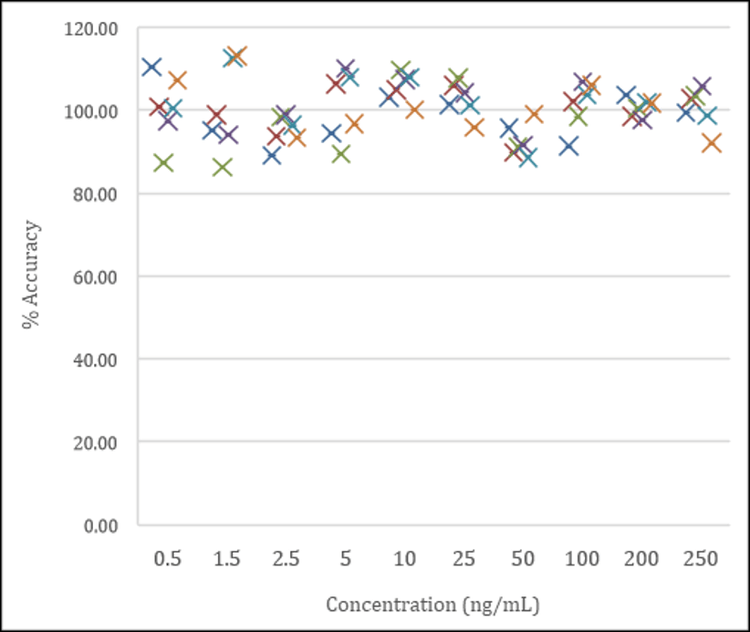
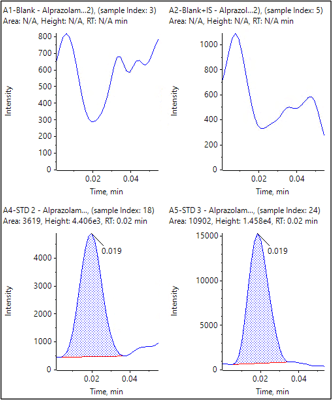
Samples analyzed in six replicates demonstrated the solid reproducibility of AEMS when combined with liquid-liquid extraction. Excellent %CVs were achieved across all concentration levels with no interference in blank human plasma samples (Figure 3). Even at the extremely short analysis time of 2 seconds per sample, the method yielded an LLOQ of 0.5 ng/mL for alprazolam in human plasma. As summarized in Table 2, the assay accuracies of 92.67–105.55% and %CVs were well within standard acceptance criteria for all tested samples. The calibration curve covered 3 orders of magnitude (0.5–250 ng/mL) and displayed linearity with a regression coefficient (r) of 0.9971 using weighting of 1/x2 (Figure 2).
Conclusions
- The Echo® MS System produced very sensitive, accurate and reproducible results for the quantitative analysis of alprazolam in human plasma.
- The extremely short analysis times (2 sec/sample) enabled rapid generation of quantitative data for high numbers of samples.
References
- Votaw VR, Geyer R, Rieselbach MM, McHugh RK.(2019) The epidemiology of benzodiazepine misuse: A systematic review. Drug Alcohol Depend. 200: 95-114.
- Moore TJ, Mattison DR, (2017) Adult Utilization of psychiatric drugs and differences by sex, age, and race. JAMA Intern. Med. 177, 274–275.
- Grohol J. (2016) Top 25 Psychiatric Medication Prescriptions for 2013.
- Rapid MS/MS analysis with Acoustic Ejection Mass Spectrometry (AEMS) - Using the SCIEX Echo® MS System to break bottlenecks in quantitative mass spectrometry throughput. SCIEX technical note RUO-MKT-02-11385-A.


