Abstract
High sensitivity analysis is key for the analysis of lipid mediators in human plasma. Here the SCIEX lipid mediator assay has been expanded and adapted to the SCIEX 7500 System. Sensitivity was compared to the QTRAP 6500+ System and an average gain in peak areas of 53 fold was observed.
Introduction
In biological samples, reliable detection and quantification of lipid mediators can be challenging because these molecules are locally acting, short-lived, and produced in small quantities (often in the femtogram to nanogram range). Detecting lipid mediators is also challenging because of the complexity and diversity of different tissue matrices which can suppress ionization and negatively affect lower limits of detection and quantification when using ESI-MS/MS. Various method development techniques can be employed to help improve the recovery and detection of analytes, such as rigorous extraction protocols or employing microflow chromatography, but these can be laborious, costly, and in some cases too time consuming to perform and maintain routinely.
LC-MS/MS analysis for the targeted quantification of lipid mediators has emerged as a powerful workflow to characterize and profile lipid mediators.1 Still, innovations that can unlock new levels of sensitivity are needed to advance the biological understanding and pathway interpretation of lipid mediator production in a range of physiological processes for personalized and precision medicine research. With technological improvements on the SCIEX Triple Quad 7500 System, the lower limits of quantification and detection have been improved compared to previously attained datafrom the QTRAP 6500+ LC-MS/MS System.1
In this report, an expanded assay panel with LLOQs down to the lower femtogram range is described. Figure 1 compares the sensitivity levels for the same sample analyzed on the QTRAP 6500+ System and on the SCIEX 7500 System. Highlighting compounds detected near their LLODs and LLOQs, and compounds simply undetected on the QTRAP 6500+ System, significant gains in sensitivity and signal to noise were observed on the SCIEX 7500 System. Several sample matrices, including NIST 1950 Metabolites in Human Frozen Plasma as well as mouse liver, brain and human serum, were analyzed to further demonstrate sensitivity improvements.
Key features of the SCIEX 7500 System for higher sensitivity lipid mediators profiling
- High-throughput quantitative analysis of lipid mediators is achieved using MRM (multiple reaction monitoring) and the Scheduled MRM™ Algorithm2
- Expanded MRM assay containing 111 lipid mediators and 16 internal standards3
- Average peak area gains of 53x for the compounds analyzed in human plasma matrix, compared to the previous generation of instruments
- Enables detection of compounds in the lower femtogram level on column in complex matrices with high precision and linearity
- Calculation of the precision, accuracy, sensitivity, and linearity method for all lipid mediators included in the assay
- SCIEX OS Software for data acquisition and processing
- Complete method provided for easy adoption3
Methods
Sample preparation: Standards were obtained from Cayman Chemical and used for optimization of the MRM transitions. Sixteen deuterium labeled internal standard MRMs were used in addition to the MRMs for 111 distinct lipid mediators, precursors, pathway markers, and metabolites.
Chromatography: Separations were performed on an ExionLC™ AD System using a Phenomenex Kinetex 2.6 µm Polar C18 column (100 x 3.0 mm). A gradient elution of methanol in 0.1% formic acid was used to separate the analytes over a 20.5 min run time at 500 µL/min.
Mass spectrometry: A SCIEX Triple Quad 7500 LC-MS/MS System – QTRAP Ready with an OptiFlow® Pro Ion Source (electrospray ionization probe) was used for data acquisition in positive and negative mode. A targeted assay was built using the Scheduled MRM Algorithm (sMRM), for quantification of the various lipid mediators. Details on the LC-MS/MS methods can be found in the supplementary information.3
Data processing: SCIEX OS Software was used for computation of calibration curves, percent CVs, percent accuracy and standard deviations.
Expanded sMRM lipid mediator library
Lipid mediators are a diverse and still expanding class of fatty acid-derived molecules. As shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2, the SCIEX lipid mediator sMRM method has now been expanded to include additional optimized subclasses of compounds, namely the ethanolamides, which include several bioactive endocannabinoids (e.g., anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol). These endocannabinoids function as neurotransmitters in the brain and peripheral tissues where they act as cannabinoid receptor agonists to inhibit neurotransmitter release and reduce inflammation.4
Because of their fatty acid structure, the majority of lipid mediators are best analyzed using negative ion mode analysis. A subset of lipid mediators, including the endocannabionoids, as well as cysteinyl leukotrienes, MCTRs and PCTRs, can be analyzed with higher sensitivity using positive ion mode analysis. Using the fast polarity switching capabilities of the SCIEX 7500 System, both polarities can be used in a single injection for the optimized detection of all lipid mediators within one assay (Figure 1).
Sensitivity gains in biological tissues
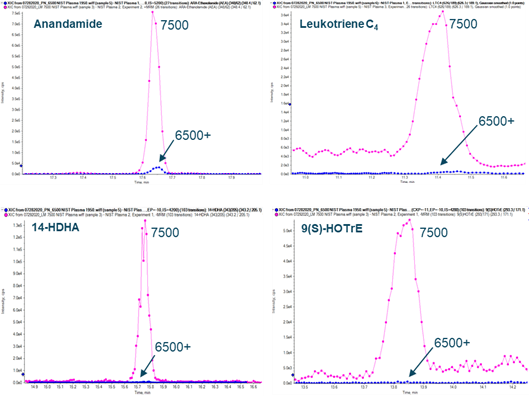
Figures 1 and 3 highlight the unique capability of the OptiFlow Pro Ion Source and D Jet™Ion Guide technology to achieve higher levels of sensitivity for lipid mediator detection in human tissues including human plasma and mouse brain, liver, and serum. Here, the Scheduled MRM Algorithm was used to optimize the method and enable the simultaneous collection of both positive mode and negative mode MRM data. The SCIEX 7500 System achieved peak area gains of >10x above the QTRAP 6500+ System in 100 µL of extracted human plasma for the endocannabinoid, anandamide, and for LTC4 (a component of slow-reacting substance of anaphylaxis) in positive mode, 14-HDHA (the pathway marker for pro-resolving maresins) and 9(S)-HOTrE (Figure 1).
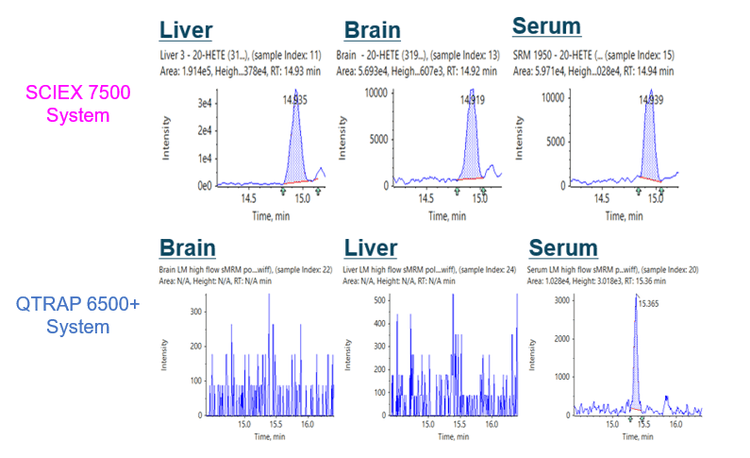
Figure 3 shows the detection of 20-HETE in mouse liver, brain, and serum when comparing the SCIEX 7500 System to the QTRAP 6500+ System. The QTRAP 6500+ System only detected this vasoactive compound in serum.
Figure 4 shows the low femtogram (on column) sensitivity and broad dynamic range (greater than 5 orders of magnitude) using the endocannabinoid, anandamide (ARA-Ethanolamide), in positive mode as an example. This lipid mediator was detected at 8.4 pg (on column) with 15% CV and 15% accuracy. It is worth noting that methods for detection of anandamide and other ethanolamide lipid mediators commonly use ammonium acetate to boost sensitivity, yet the data shown here using the SCIEX 7500 System still achieved low femtogram (on column) sensitivity without the use of ammonium acetate.

Assay statistics
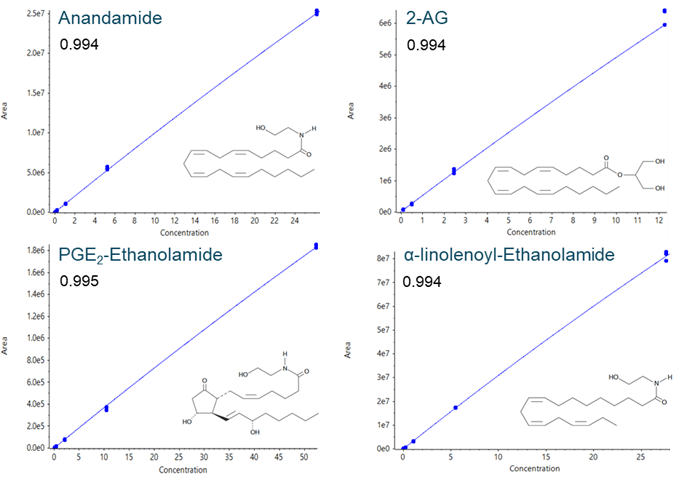
Concentration curves were generated by injecting 3 replicate injections of 7 different concentrations (in 5-fold serial dilutions) of each lipid mediator standard. Excellent linearity was observed with r2 > 0.99, and CV and accuracy < 15% (above LLOQ) and CV and accuracy < 20% (at LLOQ). Representative concentration curves are shown in Figure 5 for selected endocannabinoids and ethanolamide analytes: anandamide, 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG), PGE2-ethanolamide, and α-linolenoyl-ethanolamide.
Assay sensitivity gains
Lipid mediator profiling in human plasma is of great interest for personalized and precision medicine research. Plasma samples are easily attained and are expected to reflect the endogenous production of lipid mediators throughout the body. In addition to their inherently low abundance, other challenges in lipid mediator identification and quantification in human plasma result from matrix suppression, even when rigorous extraction protocols are used.
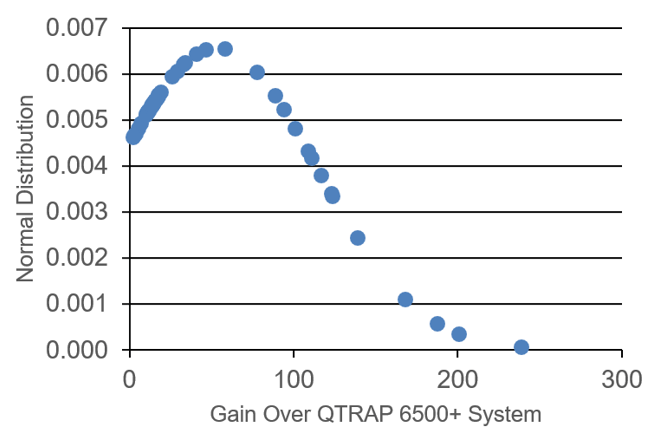
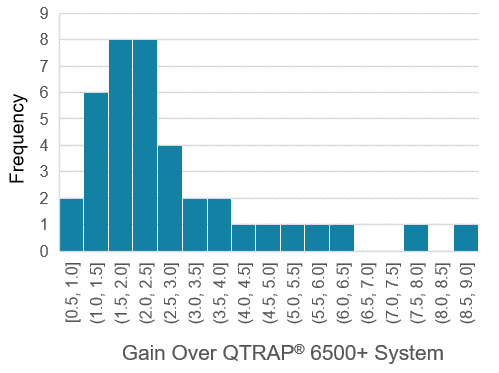
Figure 6 and 7 show the drastic improvement in sensitivity for endogenous lipid mediator analysis in human plasma when switching to the SCIEX 7500 System from the QTRAP 6500+ System. Peak areas for the compounds in this assay, observed in human plasma, were 53x higher, on average, when using the SCIEX 7500 System. They ranged from 2x higher (docosatetraenoyl-ethanolamide in positive mode) to 239x higher (13-HOTrE in negative mode).
Signal/noise ratios were also compared between the SCIEX 7500 System and the QTRAP 6500+ System and an average gain of 2.8x was observed (Figure 7).
Conclusions
A high-throughput, targeted, quantitative LC-MS/MS assay with low femtogram sensitivity was designed to monitor lipid mediators. By taking advantage of the fast polarity switching of the SCIEX 7500 System, individualized and optimized conditions could be used to monitor a wide diversity of lipid mediator species in both positive and negative ion mode within one 20‑minute MRM assay. The sMRM library was also expanded to include the endocannabinoids and other ethanolamide lipid mediators, as well as additional negative mode lipid mediators. Excellent sensitivity was obtained for all lipid mediator species with LLOQ between 8 fg and 1 pg on column and %CVs better than 20%. Sensitivity gains in human plasma were significant on the SCIEX 7500 System, with peak area increases, on average, of 53 times higher than those on the QTRAP 6500+ System.
References
- Targeted profiling of lipid mediators - multiplexed assay using the SCIEX QTRAP® 6500+ LC-MS/MS System. SCIEX technical note RUO-MKT-02-10787-A.
- Using Scheduled MRM™ Algorithm in SCIEX OS Software. SCIEX community post RUO-MKT-18-11941-A.
- Download the Lipid Mediator Quantification Method from SCIEX.com community.
- Mechoulam, R. Parker LA (2013) The Endocannabinoid System and the Brain. Annual Review of Psychology, 64, 21-47.

