Abstract
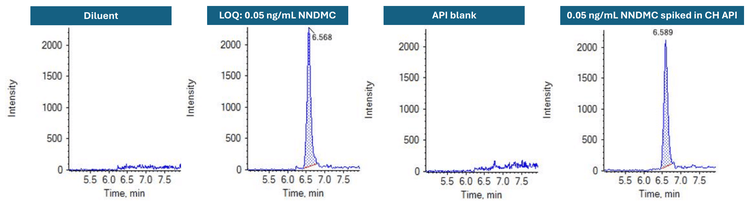
This technical note demonstrates a sensitive method for the quantitation of N-nitroso des-methyl chloropyramine (NNDMC) impurity in chloropyramine hydrochloride (CH) API using triple quadrupole mass spectrometry. A limit of quantitation (LOQ) of 0.05 ng/mL was achieved with no interference in the diluent blank and unspiked API samples (Figure 1).
Chloropyramine hydrochloride (CH) is an H1 histamine receptor antagonist primarily used to treat conditions such as bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis and conjunctivitis. It disrupts the binding of VEGFR-3 to FAK, inhibiting the phosphorylation of both proteins. This reduces VEGFR-3 and FAK's biochemical functions, suppressing cancer cell proliferation in vitro and reducing tumour growth in vivo.1 The regulation has amended the maximum permissible daily intake limit for NNDMC to 18 ng/day.2,3 This is equivalent to a maximum daily dose of less than 49 mg/day.4 Given that CH has a maximum daily dose of 49 mg/day, a nitrosamine limit of 0.367 ng/mg is required to be quantified in the API. This technical note presents a reliable and sensitive workflow to support the quantitative analysis of NNDMC in CH API below the regulation limit using the QTRAP 4500 system.
Key benefits for analysis of NNDMC using the QTRAP 4500 system
- Sub-ng/mL level of quantitation: Achieve 0.05 ng/mL LOQ for the quantitation of NNDMC.
- Quantitative sensitivity below specification limit: NNDMC was analysed at 0.05 ng/mg of API, below the calculated specification limit of 0.367 ng/mg
- Baseline chromatographic separation: Achieve accurate quantitation with baseline separation of NNDMC and CH API
- Robust analytical performance: Achieve accurate quantitative performance with %CV <3% for quantifier ion and <7% for qualifier ion was achieved at all concentration levels across a linear dynamic range (LDR) of 3.3 orders of magnitude
- Streamlined data management: SCIEX OS software, a 21 CFR Part 11-compliant platform, simplifies data acquisition and processing
Introduction
Nitrosamines are highly potent carcinogens that affect different organs. The nitrosamines are classified into various categories (class 1-5) using the Carcinogenic Potency Categorization Approach (CPCA). Here, the severity was determined based on the acceptable intake, activating or deactivating features defined in the structures. Based on the structure of NNDMC, it is placed under a class 1 category following the CPCA.
The formation of NNDMC in CH is higher due to the presence of the secondary amine.5 Since the probability of forming nitrosamine impurity is much higher, the EU has set a regulation limit of 18 ng/day. Considering the daily dosage and the regulation limit, NNDMC should be analysed below 0.367 ng/mg.
Methods
Standard preparation: Calibration curve dilutions of NNDMC were prepared across a range of concentrations in 0.1% (v/v) formic acid in water (0.05, 0.1, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 5, 10, 25, 50 and 100 ng/mL) and analyzed in triplicates.
Sample preparation: A 1 mg of CH was weighed into a suitable vessel. 1 mL of 0.1% (v/v) formic acid in water was added and vortexed thoroughly to obtain a 1 mg/mL concentration. Quality control samples were prepared by spiking samples of NNDMC in CH API at 4 concentration levels: 0.05 ng/mg, 0.1 ng/mg, 0.2 ng/mg and 0.3 ng/mg and each concentration was analyzed in six replicates.
Chromatography: Analytical separation was performed on the ExionLC system using a Phenomenex Kinetex Biphenyl (3.0 × 100 mm, 2.6 μm) column at a flow rate of 0.3 mL/min. Mobile phase A was 0.1% (v/v) formic acid in water and mobile phase B was 0.1% (v/v) formic acid in methanol. The column temperature was set to 40°C. The gradient conditions used are summarized in Table 1. A 10 μL sample aliquot was injected for LC-MS/MS analysis. The LC flow was diverted to waste for the first 6 min to prevent CH API from entering the mass spectrometer.
Quantitative performance on the QTRAP 4500 system
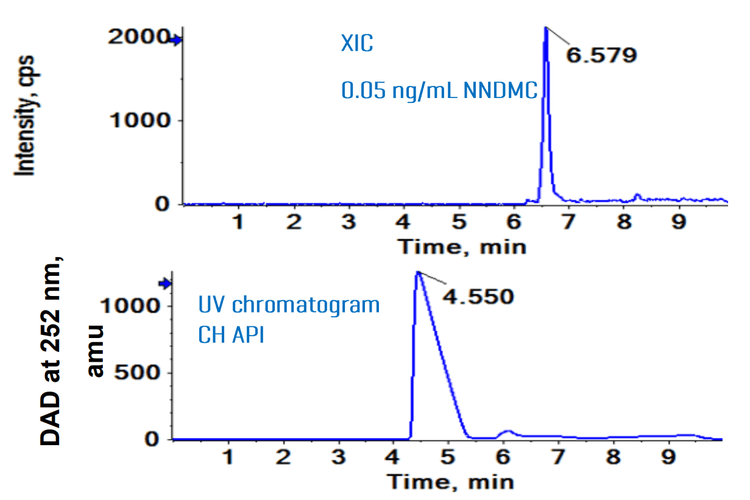
The baseline separation with ~1.8 min difference was achieved between CH and the NNDMC peaks. The NNDMC eluted at 6.579 min, while the CH API eluted at 4.55 min (Figure 2).
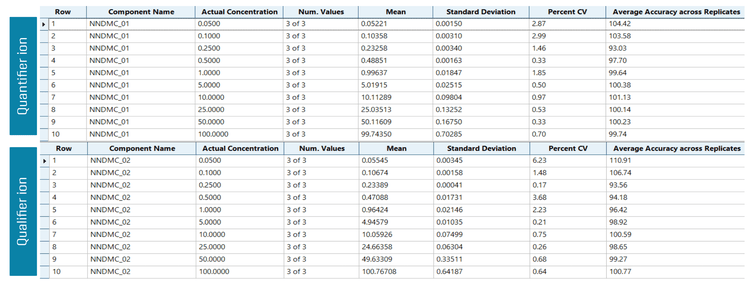
NNDMC was analyzed across the concentration range of 0.05 to 100 ng/mL. To evaluate reproducibility, each calibration standard was analyzed in triplicate.
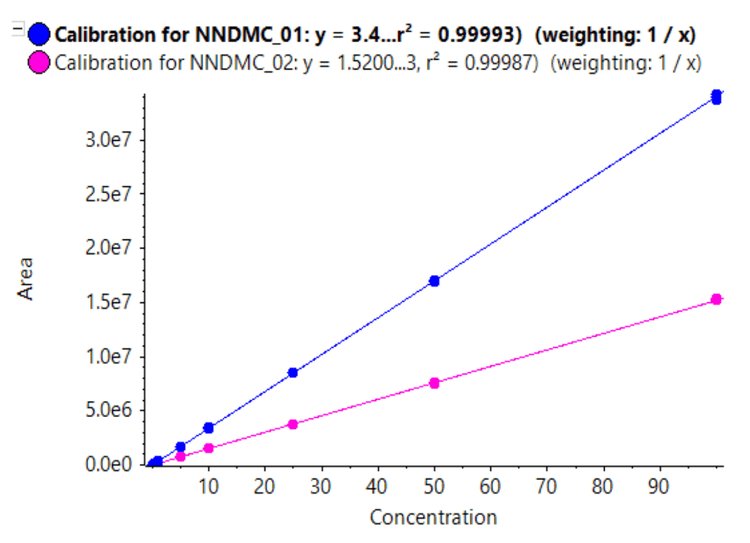
Linearity was achieved across concentrations ranging from 0.05 to 100 ng/mL with a correlation of determination (r2) of >0.999 for both quantifier and qualifier ions (Figure 3). An LDR of 3.3 orders of magnitude was achieved.
The specification limit (0.367 ng/mg) was calculated based on the maximum daily dose of 49 mg/day. The NNDMC was analyzed at 0.05 ng/mg of API, below the calculated specification limit of 0.367 ng/mg.
NNDMC was not detected in the CH API (Figure 1). Therefore, the recovery of NNDMC was calculated against the peak area of the NNDMC neat standard. The average recovery was 92.7% with a %CV of <0.1, evaluated in triplicate for neat standard and 6 replicates for the spiked sample (Table 4).
Analytical performance was evaluated based on the criteria that the accuracy of the calculated mean should be between 80% and 120% at the LOQ and between 85% and 115% at the higher concentrations. In addition, the %CV of the calculated mean of the concentration should be <20% at the LOQ and <15% at all higher concentrations.
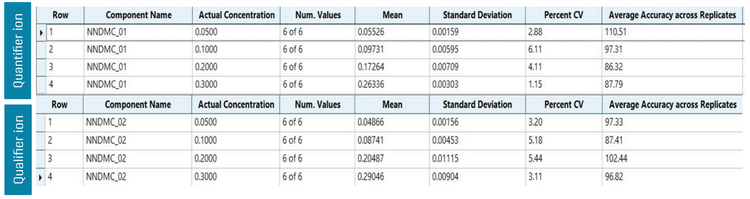
The assay accuracy was within ±7% of the actual concentration and the %CV was <7. Calculated percent accuracy and %CV values were within the acceptance criteria at each concentration level (Figure 4). In the spiked quality control samples, all the parameters met the established acceptance criteria, reinforcing the method's reproducibility (Figure 5).
Compliance-ready SCIEX OS software
Equivalent SCIEX OS software capabilities for regulated bioanalysis can be executed on the QTRAP 4500 system, ensuring high fidelity when performing method transfers while retaining critical compliance features.
SCIEX OS software is a closed system and requires records and signatures to be stored electronically, meeting the regulations outlined by 21 CFR Part 11. SCIEX OS software can open raw data files from any visible storage location within a closed network by using designated processing workstations. Figure 6 illustrates the features of SCIEX OS software used to monitor the audit trail, acquire and process data, and configure user access. The audit trail feature enables users to audit critical user actions and locks in data integrity. The Central Administrator Console (CAC) feature allows users to centralize acquisition and processing using a single platform to maximize efficiency for multi-instrument laboratories, independent of compliance standards. The configuration module allows users to assign roles and access as the administrator, method developer, analyst, and reviewer.

Conclusion
- An LOQ of 0.050 ng/mL was achieved for the quantitation of NNDMC
- Linearity was achieved at concentrations ranging from 0.05 ng/mL to 100 ng/mL with an r2 >0.999 for both quantifier and qualifier ions covering LDR of 3.3 orders
- Good quantitative performance was demonstrated with accurate and highly reproducible (%CV <7%) results on the QTRAP 4500 system
- An average recovery of 92.7% was achieved with %CV <0.1 where NNDMC was analysed at 0.05 ng/mg of API, below the calculated specification limit of 0.367 ng/mg
- The method demonstrated excellent quantitative performance in the spiked quality control samples (0.05 ng/mg, 0.1 ng/mg, 0.2 ng/mg and 0.3 ng/mg)
- A single platform for streamlined data acquisition, processing, and management with SCIEX OS software was presented
- Retain data management and compliance-readiness (21 CFR Part 11) features using SCIEX OS software to support nitrosamine analysis on the QTRAP 4500 system
References
- The Small Molecule Chloropyramine Hydrochloride (C4) Targets the Binding Site of Focal Adhesion Kinase and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 3 and Suppresses Breast Cancer Growth in vivo. National library of medicine PubMed central J Med Chem, 2009 Aug 13;52(15):4716–4724.
- Medicine for Europe, Review of NDSRI in pharmaceuticals drugs: Risk assessment, Acceptable intakes, and QSAR tools by Dr. George Johnson
- Nitrosamine impurities in medications: Established acceptable intake limits. Appendix 1: Established acceptable intake (AI) limits for N-nitrosamine impurities (version: 2024-05-31).
- Website: www.Pediatriconcall.com/drugs/chlorpheniramine-maleate/407
- Website: www.veeprho.com/impurities/n-nitroso-desmethyl-chlorpheniramine and www.chemicea.com/product/n-nitroso-desmethyl-chlorpheniramine



