LC-MS/MS solution for determination of nitrosamine disinfection byproducts in drinking water
Zhai Nannan, Jia Yanbo, Jin Wenhai
SCIEX, China
Abstract
Nitrosamine compounds in drinking water, a byproduct of the disinfection process, have been recently classified as a potential carcinogen and are thus of great interest to monitor. Here a method for simple sample preparation followed by fast and sensitive LC-MS/MS analysis has been developed that meets the NDMA limits established by the World Health Organization.

Introduction
Following the 2016 publication of the article, “Nitrosamine Carcinogen, ‘Silent Killer’ - Urgent Water Quality Standards,” nitrosamine compounds have rapidly drawn the widespread attention of the public and of those in the field of analytical monitoring. N-Nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA) is one of the known byproducts of nitrosamine disinfection and has been classified as a Group 2A carcinogen by the International Agency for Research on Cancer. The World Health Organization (WHO) has established a limit of 100 ng/L NDMA in drinking water, although no such quality standards for limiting nitrosamines in drinking water exist in China.
In response to public concern, this document presents the use of the SCIEX QTRAP® 4500 LC-MS/MS System to actively respond to national and societal appeals, partnering with the state to build multi-layered safety protections and full-process monitoring systems spanning from water sources to faucets. The method describedfor quantifying 8 nitrosamines (Figure 1) offers a simple and rapid solution for the accurate determination of nitrosamine disinfection byproducts in drinking water.
Key features of nitrosamines analysis
- Simple sample pretreatment with Agela Cleanert SPE
- Total sample runtime is less than 10 min, while still achieving separation of nitrosamine analytes on the Phenomenex Kinetex F5 stationary phase
- Sensitive detection limits below 10 ng/L, far below the standard WHO limit of 100 ng/L
- Method can be easily deployed to any SCIEX TripleQuad™ or QTRAP® System.
Figure 1: Standard LC-MS/MS chromatograms of 8 nitrosamine compounds. Detection limit below 10 ng/L, far below the standard WHO limit of 100 ng/L.
Figure 2: Standard LC-MS/MS chromatograms of 8 nitrosamine compounds. Detection limit below 10 ng/L, far below the standard WHO limit of 100 ng/L.
Experimental
Sample pretreatment: Solid phase extraction was performed using a Cleanert PEP-2 SPE (200mg/6mL, Agela Technologies) with anactivated carbon column. Procedure for SPE as follows:
- Weigh a defined quantity of ammonium bicarbonate to adjust the water pH to around 8
- Use dichloromethane and methanol in succession to activate, and use water to equilibrate the SPE column
- Load the sample at 3-5 mL/min, and rinse with ultrapure water after loading
- Elute with dicholormethane, evaporate to a defined quantity using nitrogen, and add water to make up to a defined volume for LC-MS/MS analysis to be undertaken
- Transfer a 0.25 mL aliquot to a polypropylene vial and archive the remaining volume
Chromatography: The SCIEX ExionLC™ AD System with a Kinetex F5 column (Phenomenex 2.6 μm, 100Å) was used for sample separation. Flow rate was 0.5 mL/min and injection volume was 20 μL. Gradient details are in Table 1. Typical chromatograms are shown in Figure 2.
Table 1: LC gradient program. Flow rate of 0.5 mL/min.
Mass spectrometry:
The SCIEX QTRAP® 4500 System were employed during method development and data collection. The APCI probe on the Turbo V™ Source was used in positive ion mode with the following parameters (CUR: 30psi, GS1: 50psi, NC: 5, TEM: 400°C, CAD: medium. Figure 1 shows thestructure of nitrosamines, while Figure 3 shows the parameters of the MRM transitions for each.
Figure 3: Eight nitrosamine compounds - mass spectrometry parameters. MRM transitions and optimized voltages utilized for the target nitrosamines.
Figure 4: Linear calibration curves of 8 nitrosamine compounds in water, showing good linearity (r>0.99).
Conclusions
This paper establishes a comprehensive method for the quantification of nitrosamine compounds, including sample preparation, data acquisition, and data processing using the 4500 QTRAP® System. This method provides acomprehensive solution that can be performed on any of the SCIEX Triple Quad or QTRAP Systems, saving on method development time. The advantages of this method include simple sample pretreatment, fast analysis time, and high sensitivity, allowing accurate and quantitative analysis of nitrosamine disinfection byproducts in drinking water
 Click to enlarge
Click to enlarge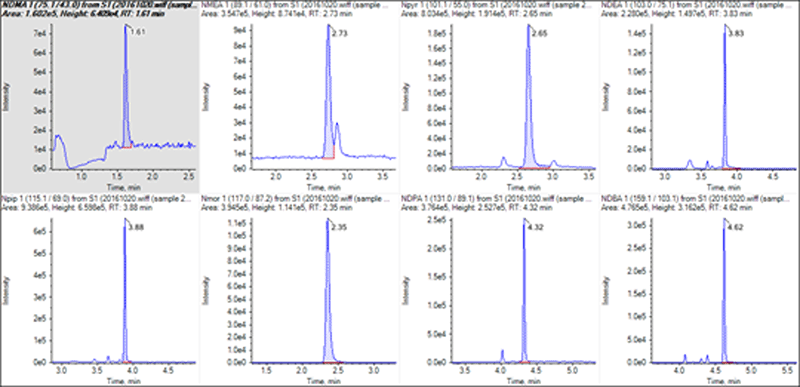 Click to enlarge
Click to enlarge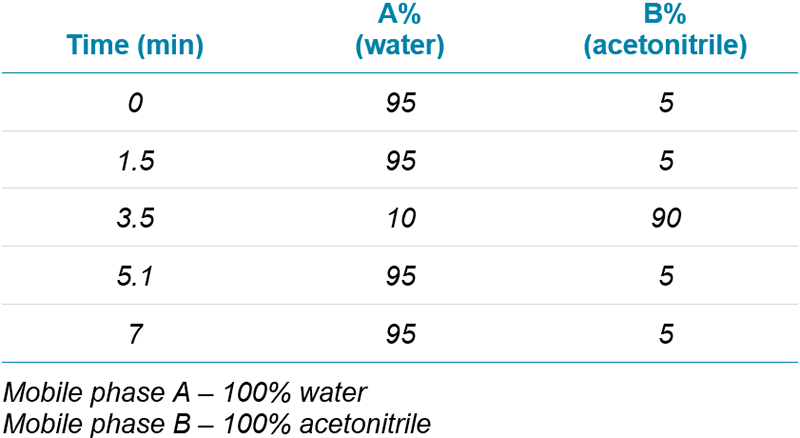 Click to enlarge
Click to enlarge Click to enlarge
Click to enlarge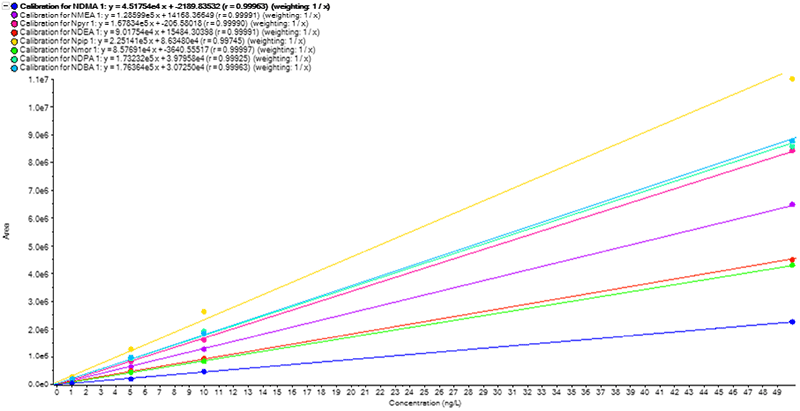 Click to enlarge
Click to enlarge