LC-MS/MS rapid quantification and screening method for 222 pesticide residues in tea
SCIEX Triple Quad™ 3500 LC-MS/MS System
Zhai Nannan, Jia Yanbo, Jin Wenhai
SCIEX, China
Abstract
The safety of tea is very important to human health due to the large rate of consumption around the world. Here, a LC-MS/MS rapid screening and detection method was established for the determination of pesticides in tea leaves using the SCIEX Triple Quad 3500 System. A QuEChERS method is used for sample pre-treatment providing high extraction recovery rate. This single injection provides high efficiency, high throughput and broad screening for the quantification of 222 pesticides in tea matrix.

Content here
Introduction
China is the world’s home of tea and is the first country in the world to discover, cultivate, make and drink tea.1 Tea has become the “coffee” of the Chinese people. Drinking tea is not only a habit, but also reflects a culture. However, driven by profit, the tea crisis is becoming increasingly important. This is mainly highlighted by the “poisoning” of tea quality2, and the repeated prohibition of “pesticide tea” has caused a large number of tea product prices to drop dramatically.
In order to ensure the quality of tea and avoid a greater crisis in the tea market, on 18 December, 2016, the Ministry of Agriculture of China and four other departments issued the “National Maximum Food Safety Pesticide Residue Limits” (GB2763-2016) (formally implemented on 18 June, 2017) which stipulated quantity limitations on 48 pesticides in tea3.
This application note focuses on the problem of pesticide residues in tea. On the SCIEX Triple Quad 3500 System, a rapid screening method of 222 pesticides has been established to provide a simple and quick solution to the problem of pesticide residues in tea.
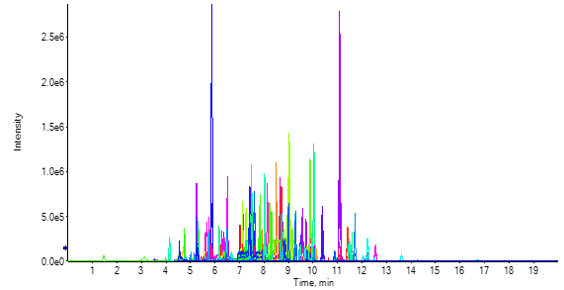
Figure 1. 222 pesticides in tea (10 μg/L).
Delivering accuracy and precision for pesticide residues in tea extracts
- This method analyses 222 pesticides simultaneously in a single injection
- Analysis time is only 20 minutes, which can provide high sample throughput
- This method provides mass spectrometric and chromatographic conditions for 222 pesticides, which saves method development time and improves work efficiency
- This method provides details for simple sample preparation for tea leaves. It has a high extraction recovery rate and is ready to use.
Methods
Sample preparation: Tea samples were extracted using the QuEChERS method, the process is detailed below:
- Start with 1g tea sample after weighing and homogenization.
- Add 5 mL water, vortex for 30 seconds, soak for 10 min.
- Add 10 mL of acetonitrile/water/acetic acid = 70/29/1 (v/v/v) and vortex for 30 seconds.
- Add QuEChERS extraction reagent
- Centrifuge at 6,000 rpm for 5 minutes.
- Take 2 mL of supernatant, add QuEChERS purification kit and shake for 1 min.
- Centrifuge at 6,000 rpm for 5 minutes.
- Take 1 mL of supernatant and dry under nitrogen.
- 200 μL acetonitrile/water = 10/90 (v/v) reconstituted residue.
Chromatography: The liquid chromatography for this workflow was performed using a SCIEX ExionLC™ System and a Kinetex Biphenyl column (100 x 3.0 mm, 2.6 µm, Phenomenex). The gradient details are outlined in Table 1. The column temperature was 40°C and the injection volume was 20 µL.
Mass spectrometry: Analysis was performed using the SCIEX Triple Quad 3500 System using the Turbo V™ Ion Source. Parameters are outlined in Table 2. MRM transitions for 222 compounds were optimized and analyzed.
Table 1: Details of the gradient elution.
Table 2: Source and mass spectrometer parameters.
Results
This workflow demonstrates a single injection method for the detection and quantification of 222 compounds within 20 minute run time (Figure 1). The method shows consistency and robustness as well as sufficient sensitivity and precision to enable high throughput analysis of tea extracts.
The method has a high extraction recovery rate, the extraction recovery rate of more than 95% of the compounds is greater than 70%, the figure below (Figure 2) details the recoveries.
The method demonstrated good reproducibility for a series of replicate injections from the same sample. The statistical performance of the percent coefficient of variation (%CV) was calculated and shows acceptable reproducibility (Figure 3).
Figure 2: Statistics on the extraction and recovery rate from tea.
Figure 3. Reproducibility of typical compounds at a concentration of 10 μg/L.
Summary
Due to the very high consumption of tea in many cultures including china, the safety of tea is very important to human health. Here, a LC-MS/MS rapid screening and detection method was established for the determination of 222 pesticides in tea leaves using the SCIEX Triple Quad 3500 System. This method uses the QuEChERS method for sample pre-treatment. It was shown to have both a high extraction recovery rate and good reproducibility, and thus can be used for the determination of pesticide residues in actual tea samples. In addition, this method enables the detection of 222 pesticides in a single injection providing high efficiency, high throughput and broad screening for analytes of concern.
References
- Lozano A, Rajski Ł, Belmonte-Valles N, Uclés A, Uclés S, Mezcua M, Fernández-Alba AR. (2012) Pesticide analysis in teas and chamomile by liquid chromatography and gas chromatography tandem mass spectrometry using a modified QuEChERS method: validation and pilot survey in real samples. J Chromatogr A. 1268: 109-22.
 Click to enlarge
Click to enlarge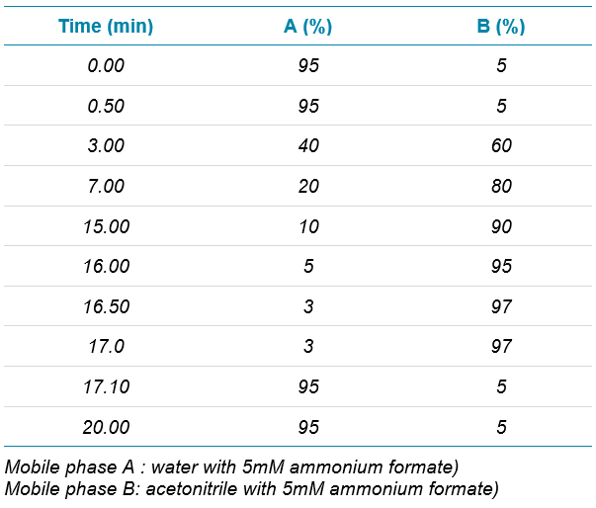 Click to enlarge
Click to enlarge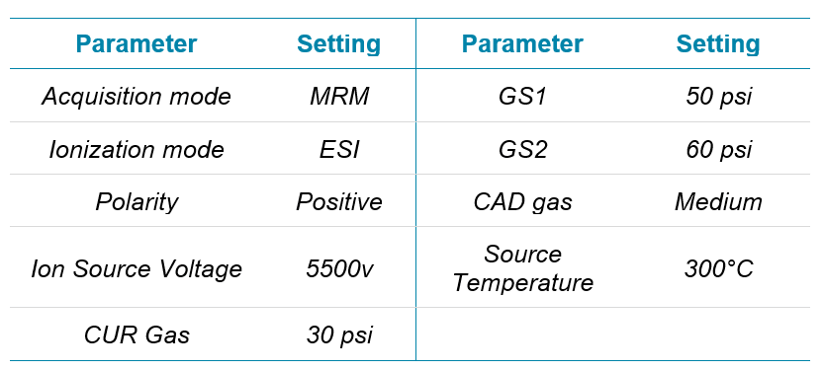 Click to enlarge
Click to enlarge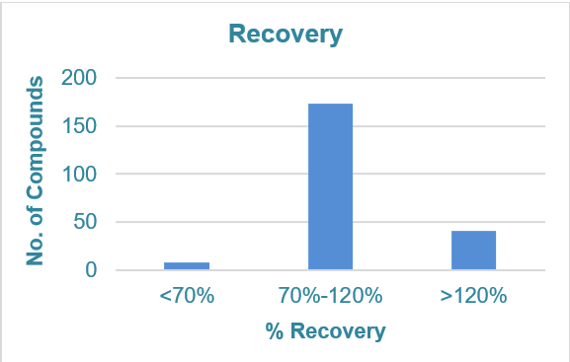 Click to enlarge
Click to enlarge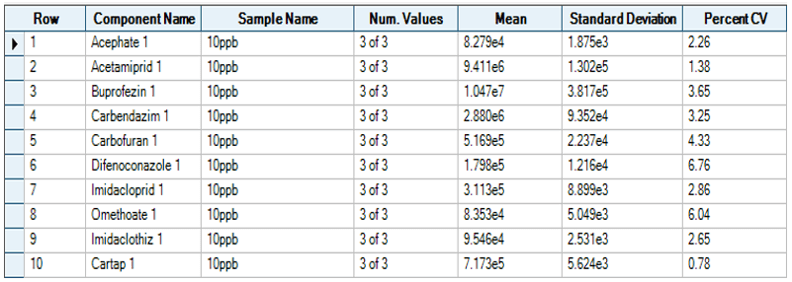 Click to enlarge
Click to enlarge