- Home
- Life Science Research
- Metabolomics
- Automated targeted screening of hundreds of metabolites - using an Accurate Mass Metabolite Spectral Library with SCIEX OS Software
Automated targeted screening of hundreds of metabolites
Using an Accurate Mass Metabolite Spectral Library with SCIEX OS Software
Abstract
The field of metabolomics is rapidly evolving and LC-MS is becoming increasingly important. Two main workflows are used, untargeted discovery approaches to extract and identify a wide range of compounds in biological samples, and targeted approaches where the dataset is interrogated for a set of known metabolites to quickly generate quantitative biological results. Here the Accurate Mass Metabolomics Spectral Library (AMMSL) is described for global targeted screening. This library contains 650 metabolites across a variety of pathways such as TCA cycle, BCAA degradation/synthesis, glycolysis, urea cycle and across many compounds classes such as amino acids, bile acids, sugars, nucleotides, organic acids including many natural and non-natural products (including common drugs). A streamlined workflow using SCIEX OS Software for rapid identification and quantification of metabolites from the large sample sets followed by statistical analysis using MarkerView software is demonstrated.
Introduction
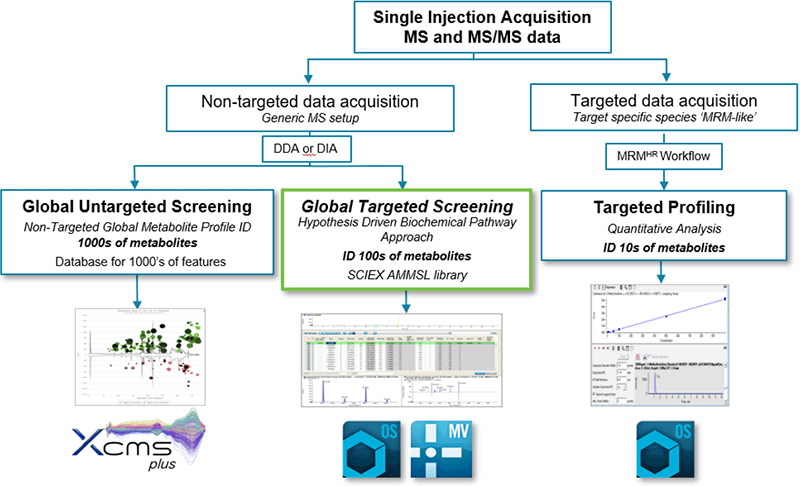
For untargeted metabolomics, there are two main approaches to mine and interrogate the data: the pure discovery route by efficiently extracting the most peaks to cover a broad range of metabolites and the targeted route whereby one interrogates for a set of known metabolites to quickly generate quantitative results. LC-MS is essential for metabolomics workflows because of its versatility, soft ionization and coverage of metabolites1 as well as being amenable to automation and high throughput. As the field of metabolomics has rapidly evolved so has the technology and these advancements have allowed for more powerful data acquisition strategies. The powerful data dependent workflow of the SCIEX QTOF systems means that the user can collect high resolution, accurate mass MS and MS/MS data in a single injection. Once the data has been collected in an unbiased way (untargeted analyses), one can now search the data either using a targeted approach for known metabolites or metabolites, pertaining to a specific pathway or classes – known as targeted metabolite screening. Or one can search the data more broadly looking for unknowns in an untargeted fashion – known as untargeted metabolite screening. If a very specific set of metabolites are of interest, these can be studied in a very targeted focused workflow to obtain highest quality quantitation using a targeted profiling approach (Figure 1).
Here, a streamlined workflow is presented using the global targeted screening approach followed by data processing using SCIEX OS Software with a high resolution, accurate mass metabolite spectral library (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Metabolite workflows using SCIEX QTOF LC-MS/MS Systems. Collect data using an untargeted approach (DDA or DIA) and process the data using the accurate mass metabolite spectral library.3 Any metabolite identification is done upfront and confirmed using TOF MS, RT, isotope pattern and MS/MS criteria. Then data can be transitioned for statistical analyses, quantitation and/or reporting.
Key features of targeted metabolite screening
- Fast acquisition of high resolution, accurate mass MS and MS/MS data on the SCIEX QTOF Systems enables a single injection data acquisition strategy
- Easy to use, targeted data processing using SCIEX OS Software enables data to answers in minimal clicks
- Accurate mass metabolite spectral library contains over 600 compounds from most studied biochemical pathways and compound classes across many species/organisms
- Compound identification with high confidence based on automatic evaluation of:
- Retention time, mass accuracy, isotope pattern and MS/MS
- Reduce data review time, get to biological answers faster
- Easy transition to quantitation & reporting
Value of the Metabolite Library
Metabolomics profiling studies are often complicated through various sources of endogenous and exogenous compounds, such as medications, extractables, leachables, pesticides, illicit drugs, foods, natural products, PFAS, and more. This library workflow allows a focused search for the endogenous biological metabolites including a large number of polar metabolites. The library is also highly curated and developed on SCIEX QTOF instruments for highest quality spectral matching.
The high resolution accurate mass metabolite spectral library contains 650 metabolites which are found across various biochemical pathways, compound classes and across many species. The library contains compounds from the following classes:
- Amino acids
- Bile acids
- Nucleotides / Nucleosides
- Carboxylic acids
- Sugars
- Catecholamines
- Organic acids
- Polyamines
- Simple lipids
- Steroids
- Vitamins
- Common drugs
- Common plant metabolites
Figure 2. Global targeted screening workflow using SCIEX OS Software and the Accurate Mass Metabolomics Library. After data acquisition using the SCIEX QTOF or TripleTOF® Systems, data can be rapidly processed in SCIEX OS Software to obtain identification and quantitation information on metabolites across the sample set. After scoring, confident identifications can be quickly reviewed and confirmed. Quantitation information on the identified metabolites can then be exported to MarkerView™ Software for statistical analysis.
Workflow for targeted metabolite screening
The workflow for targeted metabolite screening is highlighted in the Figure 2. Data is acquired using the SCIEX accurate mass systems, both data dependent and data independent workflows are used in this workflow.3 In SCIEX OS Software, using information from a focused library, information for all compounds in the library is extracted.
Extracted Ion Chromatograms (XICs) are generated for all metabolites in the library, based on thresholds set by the user such as formula and expected retention time of all target analytes. The MS and MS/MS information is automatically evaluated if the detected XIC signal exceeds the user defined intensity threshold or signal-to-noise (S/N) (Figure 3). Data processing results are ranked based on 4 selectivity criteria, to provide a high degree of confidence in assigning compound identifications to detected compounds:
- Retention time matching
- Mass accuracy
- Isotope pattern fit
- MS/MS library searching
The confidence settings can be set for each of the criteria, then results are easily reviewed for metabolite through the easy-to-navigate user interface (Metabolite confidence in Figure 3).
After metabolites are identified, the identifications and the quantified areas from either the MS or MS/MS data can be exported to MarkerView Software for statistical analysis across the sample set. Principal component analysis or T-tests can be used to find the metabolites that differentiate the samples. The workflows are simplified by the fact that every variable in the loadings plot has a metabolite identification from the spectral library searching step.
Figure 3. Review data in SCIEX OS Software. The data can now be reviewed and any matches against the database can be evaluated. The traffic light system allows easy review and a user can filter compounds identified with highest confidence by selecting all the green rows meaning these compounds passed the confidence settings.
Conclusions
The SCIEX accurate mass metabolite spectral library contains 650 metabolites across a variety of pathways such as TCA cycle, BCAA degradation/synthesis, glycolysis, urea cycle and across many compounds classes such as amino acids, bile acids, sugars, nucleotides, organic acids including many natural and non-natural products (including common drugs). In the second revision of the library, 93 additional polar metabolites were added.
A streamlined workflow using SCIEX OS Software allows rapid identification and quantification of metabolites from the large sample sets, with intuitive data review. Explore the XICs, the MS and MS/MS matching information to quickly confirm metabolite identifications. Finally, quantitative results can be exported to MarkerView Software for statistical analysis to determine the metabolites with biological interest.
References
- Zhou B, Xiao JF, Tuli L, Ressom HW. (2012) LC-MS-based Metabolomics. Molecular Biosystems, Feb8(2): 470-81.
- AMMSL available via purchase of a license.
- Improved metabolite identification in a single injection using data independent analysis for untargeted metabolomics - using the TripleTOF® 6600 System and SWATH® Acquisition. SCIEX technical note RUO-MKT-02-10617-A.
Acknowledgements
Thanks to Emmanuel Varesio and Gerard Hopfgartner from University of Geneva, Switzerland. The first generation library (AMMSL 1.0) was collected in collaboration with Professor Gerard Hopfgartner at the University of Geneva and his team. The spectra were transferred to SCIEX and the library was built in the LibraryView™ Software framework. Additional metabolites (~90 new metabolites) have been added to this next revision of the library (AMMSL 2.0).
 Click to enlarge
Click to enlarge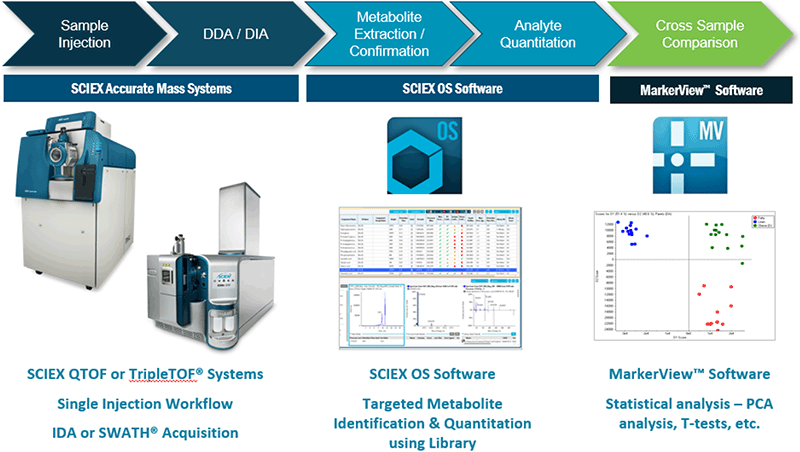 Click to enlarge
Click to enlarge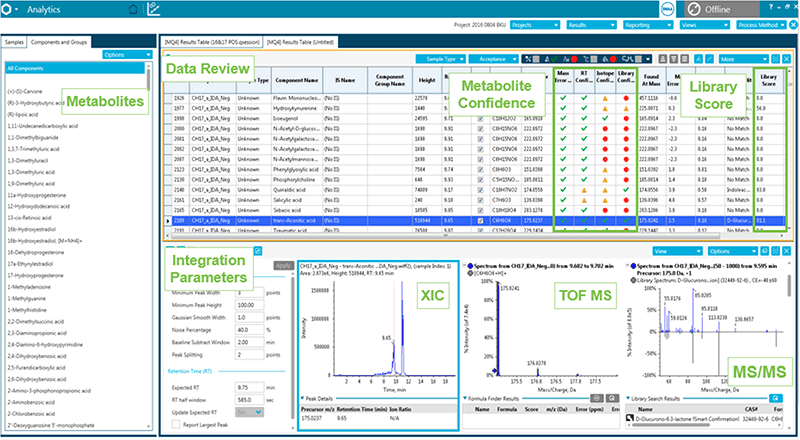 Click to enlarge
Click to enlarge