Ultrahigh pressure liquid chromatography for analysis of therapeutic drugs in whole blood
Repeatability performance of the ExionLC 2.0 system
Adrian M. Taylor1 and Daniel Blake2
1SCIEX, Canada; 2SCIEX, United Kingdom
Abstract
LC-MS/MS is commonly used to analyze clinical research samples involving the detection and quantification of drug compounds in whole blood. Complex and expensive extraction steps have historically been considered necessary due to the nature of whole blood and the analytical challenges whole blood poses. More recently, rapid methods that use a simple protein precipitation step followed by direct injection, has proven to provide precise and accurate performance down to the required levels. The chromatographic performance is essential to allow for the use of the rapid method. In this technical note, the performance of this assay using the ExionLC 2.0 system, was investigated. The method displays excellent accuracy, precision and robustness.

Introduction
Tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) has become the analytical choice for the analysis of therapeutic drug compounds in clinical research samples. Many instances require monitoring these compounds in whole blood, which poses a challenge in managing matrix effects. Matrix effects can cause ionization suppression and/or enhancement, which can reduce the precision and accuracy of quantification. Many traditional methods overcome matrix effects by using time-consuming and expensive extraction methods.1-4 More recently, simple and rapid methods5 have been developed that can be used to analyze drug compounds in whole blood. These methods meet benchmarks for assay performance, while reducing cost and time investment.
To be successful, tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) experiments must be combined with a method that achieves high-quality upfront compound separation. This is typically achieved using liquid chromatography (LC) and the chromatographic performance is crucial to implement a rapid and robust method. In this technical note, the performance of a method for the analysis of therapeutic drugs in whole blood using the ExionLC 2.0 system for chromatographic separation, was investigated.
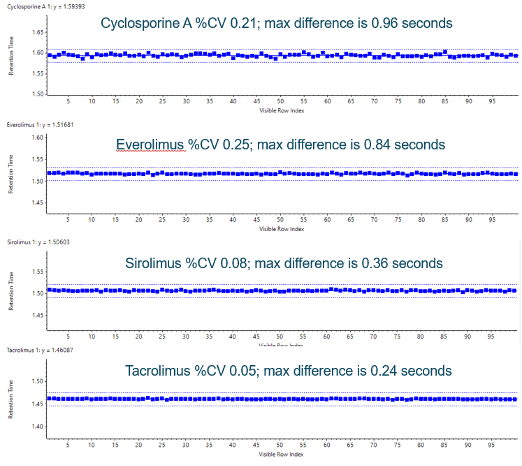
Figure 1. Retention time precision. Retention time variability of the ExionLC 2.0 system for the therapeutic drug compounds for 100 injections is shown. It exhibited good retention time stability well within a mean regression of ±1% deviation (dashed lines).
Key features of therapeutic drug quantification using the ExionLC 2.0 system
- Fast and robust assay for the detection of therapeutic drugs in whole blood
- Simplified sample preparation using protein precipitation
- Reproducible quantification using the ExionLC 2.0 system with the SCIEX Triple Quad 4500 system
- High-pressure, dual, serial piston pump rated to 860 bar at flow rates of 0.001 to 2 mL/min for maximum flexibility
- Precise and stable solvent flow delivering less than 0.5% RSD retention time variation (Figure 1)
- Excellent accuracy, precision and robustness achieved.
- Accurate and precise quantification results with linear coefficient of determination performance (r2) > 0.99 and coefficient of variation <10% for all concentration levels studied.
 Click to enlarge
Click to enlarge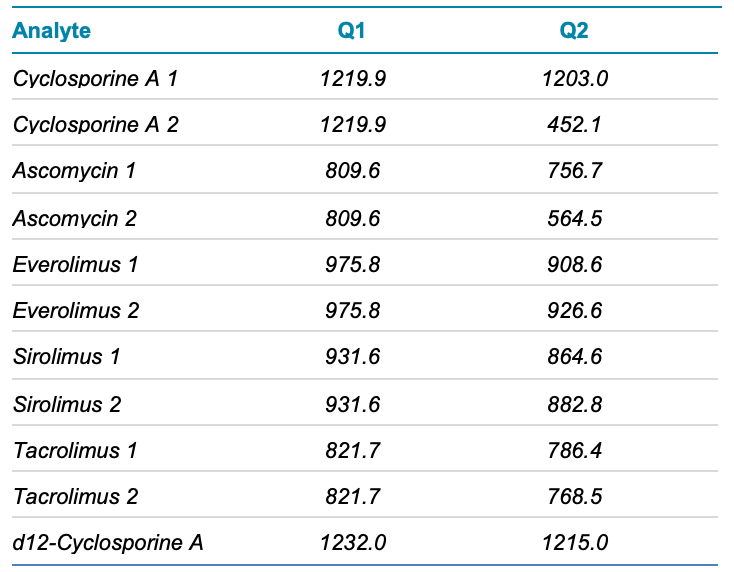 Click to enlarge
Click to enlarge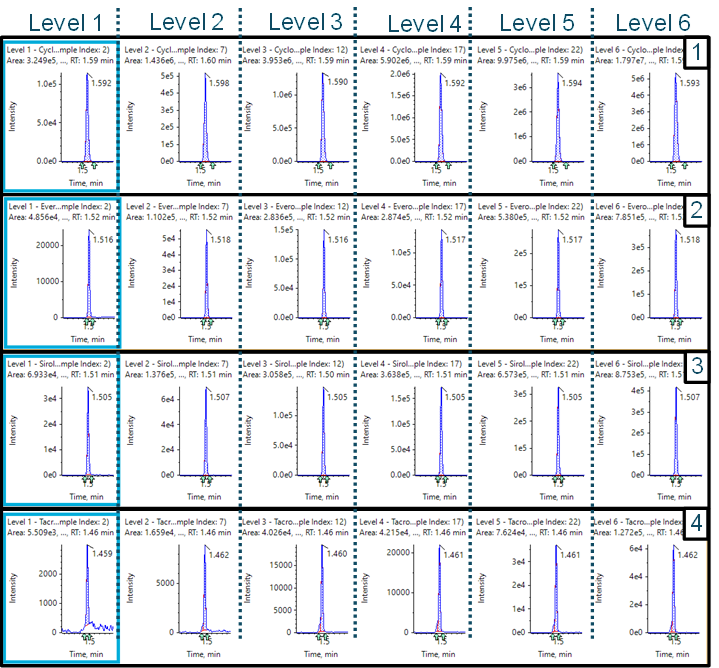 Click to enlarge
Click to enlarge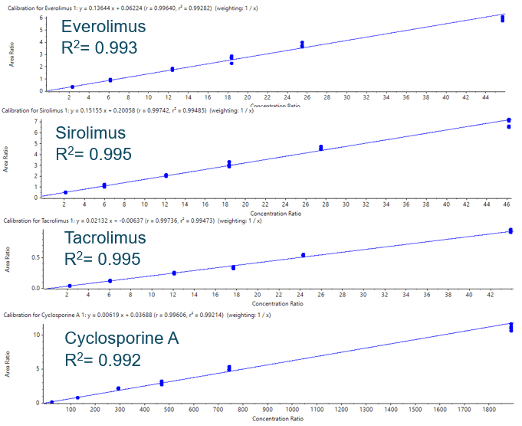 Click to enlarge
Click to enlarge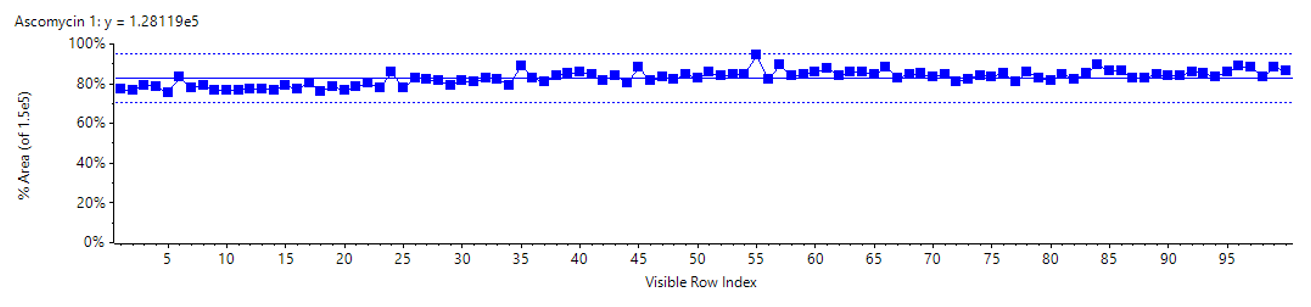 Click to enlarge
Click to enlarge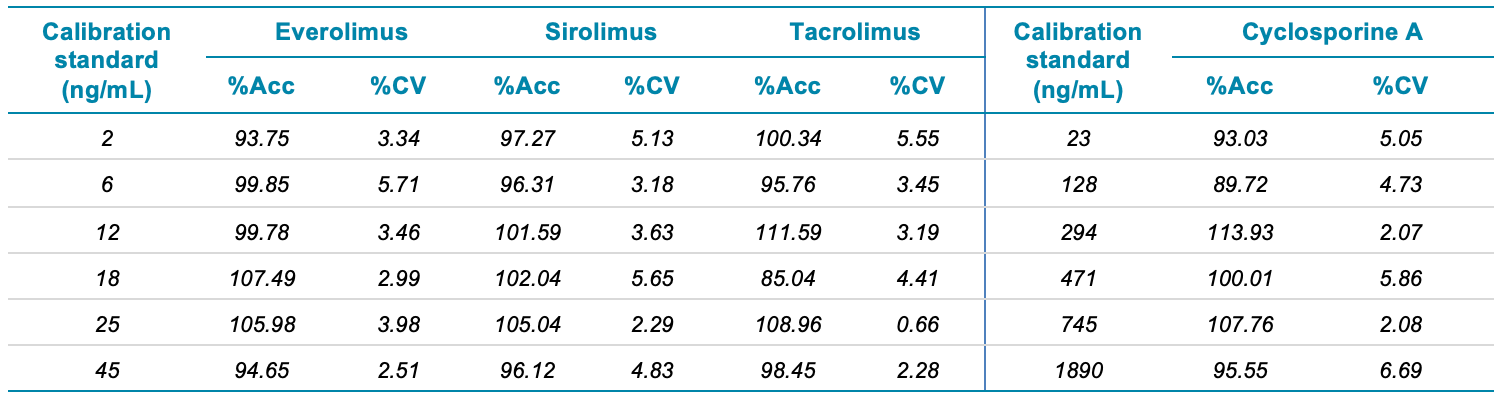 Click to enlarge
Click to enlarge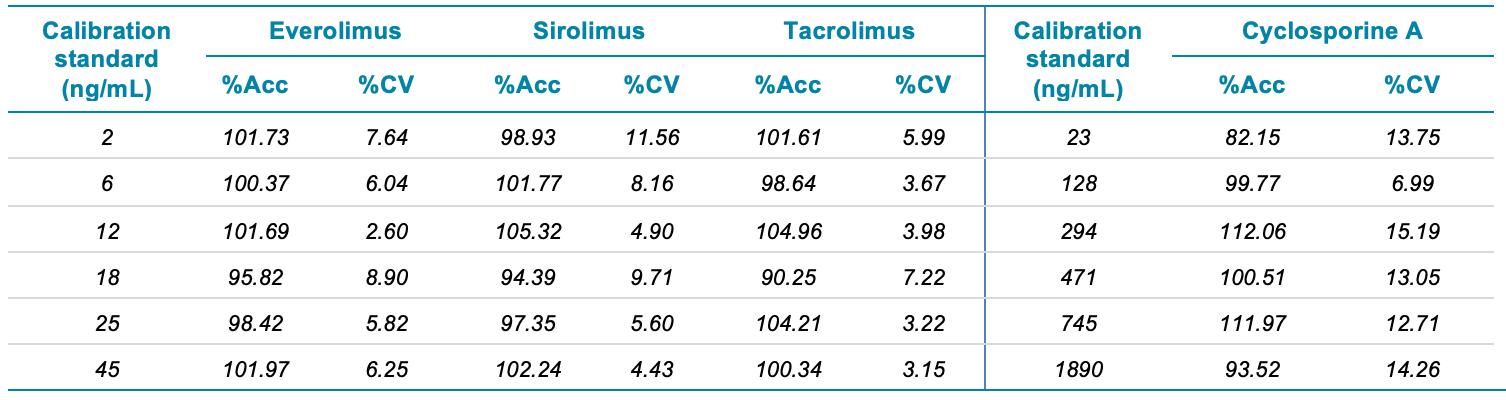 Click to enlarge
Click to enlarge