Abstract
Selective, sensitive and reproducible methods for the detection and quantitation of nitrosamine compounds in both losartan and ranitidine using the SCIEX QTRAP 4500 System are described. These methods require minimal sample preparation, provide sufficient quantitative sensitivity in the presence of the API and therefore are suitable for incorporation into a QC environment
Introduction
In recent years, there have been several high profile drug recalls of angiotensin II receptor blocking saratan class drug (valsartan, losartan, irbesartan), due to contamination of the final drug products with potentially genotoxic nitrosamine compounds, including n-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA). More recently in September of 2019, the US FDA announced the discovery of low levels of NDMA in the H2 blocker ranitidine, generic for Zantac, which is sold as an over-the-counter medication used to treat heartburn and GERD. This resulted in the recall by some manufacturers of this product, and the recommendation of some regulating agencies (Health Canada) that all products containing this medication be recalled. Drug product contamination and subsequent recalls pose obvious health risks to consumers, and significant expenses to producers. Implementation of sensitive, selective analytical techniques can help prevent issues such as these from happening in the future. Here, two analytical methods are described for the analysis of genotoxic nitrosamine compounds in the respective active pharmaceutical ingredients (losartan and ranitidine) that easily meet the sensitivity requirements for these important contaminants.
Nitrosamine compounds have various recently revised maximum acceptable daily intake levels set by the US FDA ranging from 26.5 ng/day for n-nitrosodiethylamine (NDEA) to 96 ng/day for NDMA. Because the daily dosage of a drug can vary, an analytical method must be at least sensitive enough to detect potential contaminants that correspond to acceptable exposure in the highest recommended daily dose. See the equation below for a mathematical description of required assay detection limits.
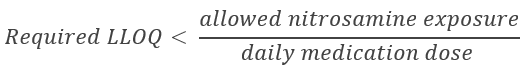
As can be seen from the above equation, larger daily doses and lower allowed exposure limits translate to lower required assay lower limits of quantitation (LLOQ’s).
Both of the assays described are performed on the SCIEX QTRAP 4500 LC-MS/MS System, coupled to an ExionLC AD System. Losartan and ranitidine elute under different chromatographic conditions, so different HPLC gradients and stationary phases are used to prevent the very large concentrations of the API’s from coeluting with the analytes of interest which could potentially cause ionization suppression, and lead to reduced sensitivity or inaccurate quantification.
Key features of the QTRAP® 4500 System
- Sensitivity and selectivity that can easily meet the needs of routine analysis for these contaminants in multiple matrices
- Simple sample preparation and optimized chromatography to easily achieve required sensitivity levels
- Industry proven “workhorse” level reliability and robustness
Methods
Sample preparation and chromatography:Due to differences in the two medications and dose levels, slightly different preparations were used.
Ranitidine: 100 mg of the powdered API was dissolved in 2 mL of 10% methanol in water. For analysis of the drug product, four 150 mg tablets were crushed and dissolved in the same diluent as the API to a concentration of 50 mg/mL. The mixture was vortexed for 15 minutes and sonicated for another 10 minutes. The mixture was then centrifuged at 4000 rpm for 5 minutes and the supernatant was filtered through a PVDF filter.
Losartan: API powder was weighed out and diluted to a final concentration of 40 mg/mL in 10% methanol in water.
Chromatography:Separations were performed using the ExionLC AD System with a UV detector. See Supplementary Information for details on the chromatographic conditions for both methods.1
Mass apectrometry:The QTRAP 4500 System was operated in positive polarity using the atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (APCI) probe on the Turbo V™ Ion Source for both assays. For ranitidine, only NDMA was assayed. For losartan, the suite of nitrosamines was assayed. Please see Supplementary Information for instrument settings, MRM transitions and source conditions for both methods.1
Results
Standard curves, replicates and QC’s were prepared and analyzed as partial method validations to demonstrate the method’s suitability for implementation in a regulated environment for routine analysis of drug substance and product.
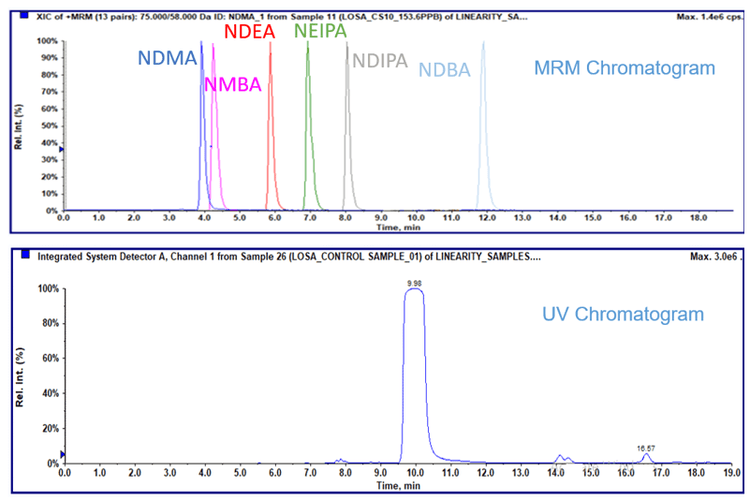
Nitrosamines in losartan
An example of the separation achieved for nitrosamine compounds in the presence of losartan API is shown in Figure 1.
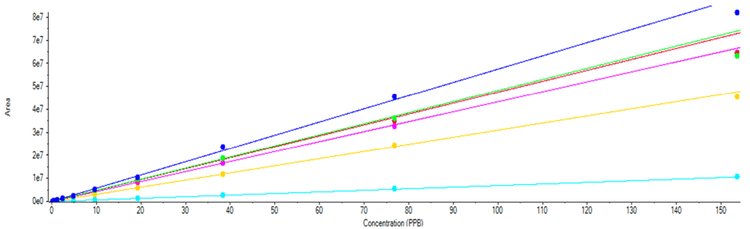
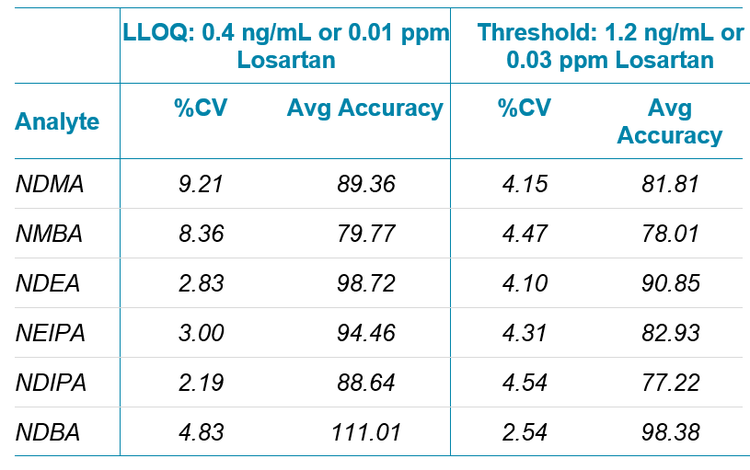
Standard curves were run from 0.2 ng/mL to 153.6 ng/mL for all of the nitrosamine compounds in this assay, which corresponds to .005 to 3.84 ppm with regard to losartan (Figure 2). The LOD for all six compounds was evaluated to be 0.2 ng/mL, with the LLOQ being 0.4 ng/mL. Precision and accuracy of the method were measured by preparing 6 replicate spikes of the suite of compounds at the LLOQ and at the current action threshold for this class of compounds (Table 1).
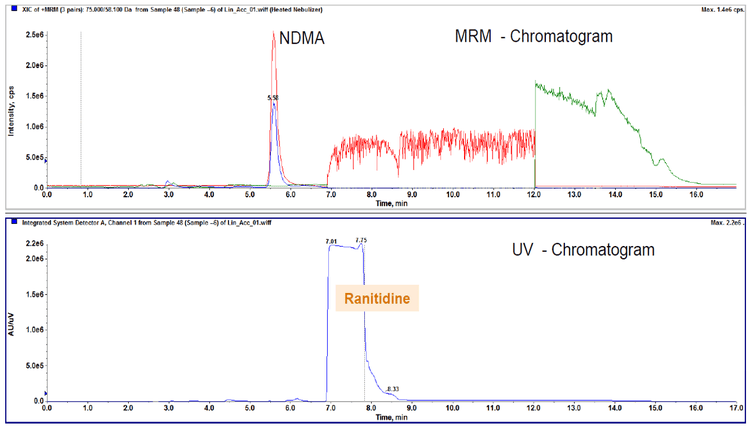
NDMA in ranitidine
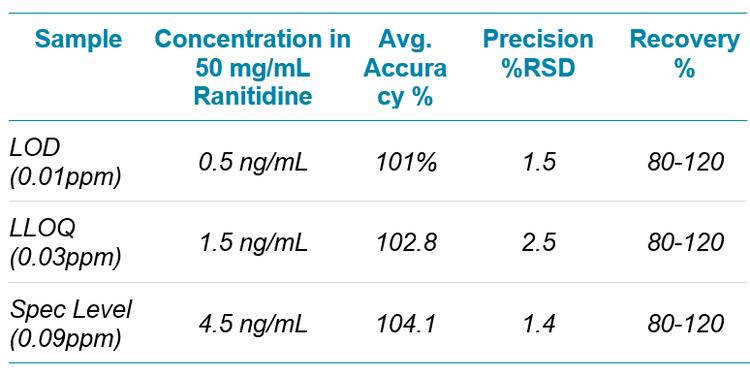
An example chromatogram showing NDMA and ranitidine elution is shown in Figure 3. A 10 point standard curve was run from 0.5 ng/mL to 500 ng/mL, which corresponds to 0.01 to 10 ppm in 50 mg of the API. The LLOQ of NDMA was evaluated to be 1.5 ng/mL, which corresponds to 0.03 ppm in 50 mg of the API. A linear calibration curve was observed over the range. Precision and accuracy was evaluated at three concentrations levels: the LOD, LLOQ and specification limit level. The recoveries at all three levels were within 80-120% of nominal with good precision, and are listed in Table 2
Conclusions
Selective, sensitive and reproducible methods for the detection and quantification of nitrosamine compounds in both losartan and ranitidine are described. The sensitivity of the SCIEX QTRAP 4500 System allows quantification below current established limits for these compounds in the respective active pharmaceutical ingredients, without extensive sample preparation. These methods are suitable for incorporation into a quality control environment to support lot release analysis for these important medicines.
References
Related content
- Rapid Analysis of Genotoxic Nitrosamines by HPLC-MS-MS. SCIEX technical note RUO-MKT-02-9127-A.
- Highly Selective and Sensitive Method for Quantitation of Nitrosamines in Valsartan Drug Substance. SCIEX technical note RUO-MKT-02-11212-A.
