Gaining more information upfront about a therapeutic can reduce risk and late-stage failures by providing critical insights on post-translational modifications (PTMs), or the effects of growth conditions on your cell line.
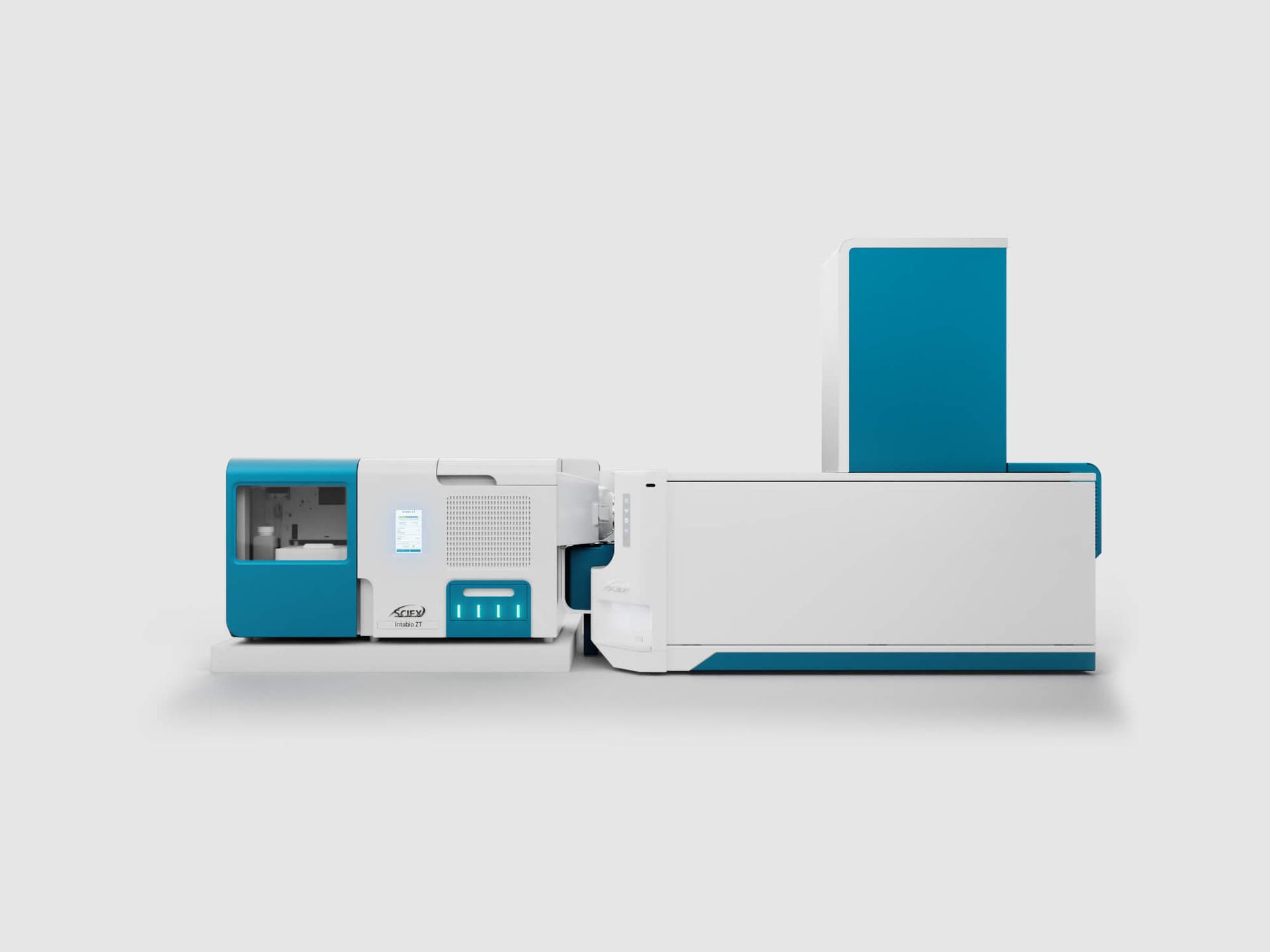
For this case study, the team encountered multiple CMC programs where a dark brown color at the viral inactivation stage was observed and which became darker at higher concentrations. Learn how the Intabio ZT system was utilized to rapidly uncover the underlying cause.